When using UEFI, at some point, if you receive an error screen saying — Selected boot image did not authenticate, then it means UEFI is having a problem figuring out if the boot image has been tampered with. UEFI offers Secure Boot, and if the boot image seems invalid, you will not be allowed to boot into the computer. You may also use endpoint encryption; the software cannot validate the certificate. In this post, we will suggest some methods to resolve the problem on Windows 11/10.
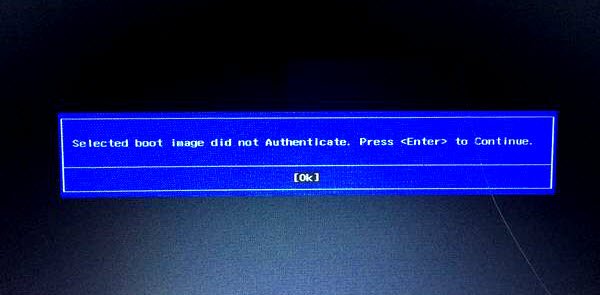
Selected boot image did not authenticate
The first thing you need to check if the error has a reference to any software that you might have for encryption. If yes, then follow the first method; else, move to the third.
- Disable Encryption Tool
- Disable Secure Boot
- Perform Startup Repair
If you are in a hurry, the second method is for you.
1] Disable Encryption Tool
There are reports that some encryption tools like ESET Endpoint Encryption will not let you boot into the computer if the system manufacturer doesn’t include the correct certificates as a part of the UEFI BIOS. As there is no way to bypass it, disable Secure Boot to boot into the computer. Get in touch with your IT admin or uninstall the software completely, and later enable the UEFI to see if it works.
2] Disable Secure Boot
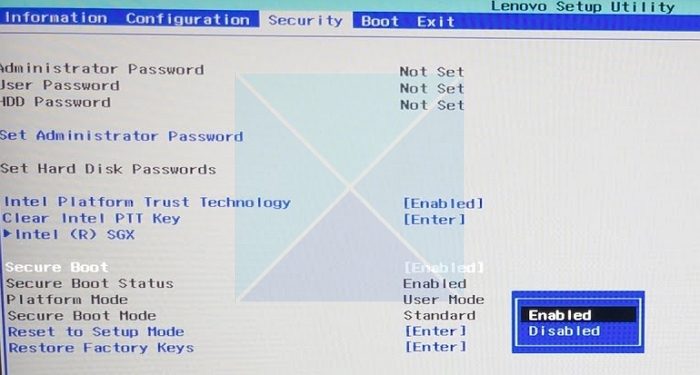
If you are using UEFI, it is recommended to use Secure Boot. However, if it is not letting you boot into the device, it’s best to disable Secure Boot from your System BIOS, save the changes, and restart the computer. The system will proceed to boot as usual. However, it’s only a temporary solution. It will make the Selected boot image did not authenticate problem go away.
3] Perform Startup Repair
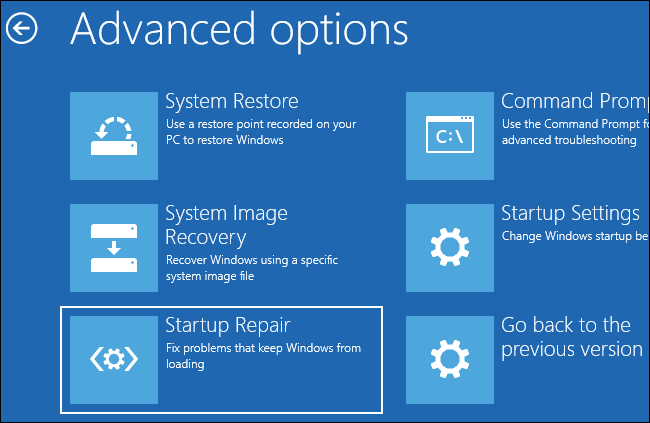
While disabling Secure Boot is an option, it’s not something many will agree; UEFI is there for a reason. So, performing Startup Repair is a better option. I have seen reports in the forum, which have worked for a few. Make sure to keep the Secure Boot option ON and legacy mode disabled.
- Boot into the Advance Recovery Mode
- Select Troubleshoot > Startup Repair
- Follow the on-screen instructions and finish the repair.
- Then, check if the block is gone once the reboot is complete.
Secure Boot ends with loading a certified Bootloader of the OS into memory. The digital certificate comes from the OEM or the Enterprise. To completely resolve the problem, contact IT admin or Microsoft support.
What is secure boot in Windows PC
Secure Boot is a built-in security measure found in Windows computers. Its purpose is to safeguard against unauthorized code execution during the boot-up sequence. Allowing only digitally signed and authenticated bootloaders, kernels, and boot managers to run effectively blocks potential threats such as malware and rootkits. The UEFI firmware plays a vital role in verifying these signatures, ensuring the system’s integrity, and effectively countering low-level attacks.
Should I disable TPM in Windows?
Disabling TPM in Windows should be done cautiously and only when necessary. TPM provides hardware-based security, protecting sensitive data and defending against unauthorized access. While it might be disabled for troubleshooting or specific tasks, its benefits for overall system security should be considered before making the decision.