In this post, we will see how to show Hidden Files, Folders & Drives along with Protected operating system files in Windows 11/10/8/7, via File Explorer Options in the Control Panel or by using the Command Prompt and PowerShell.
On most days, you would not want to be bothered by the hidden Windows files on your computer. After all, the last thing that an average Windows user needs is some more data to deal with. On some rare instances though, or if you know what you’re getting yourself into, you may need access to these hidden files to make changes to Windows apps or system settings. These hidden files aren’t readily viewable when you open their parent folder(s) in the File Explorer. Ee will walk you through the steps needed to be taken to show hidden files and folders using the Explorer Options, Windows Command Prompt and the PowerShell, two of the strongest methods for the purpose.
Show Hidden Files & Folders in Windows 11/10 via Explorer Options
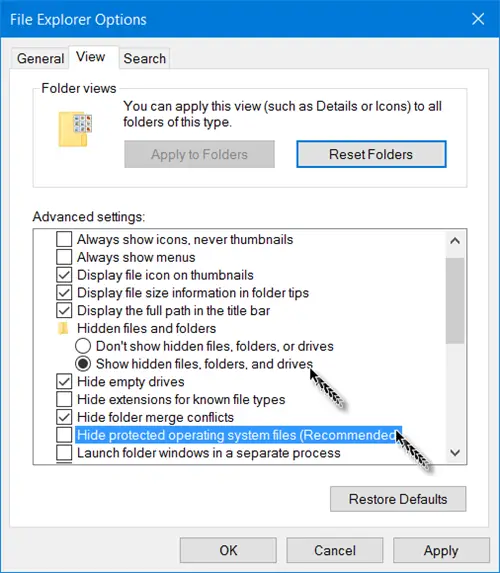
You will have to open the Control Panel and then select the File Explorer Options in Windows 11/10. File Explorer Options is referred to as Folder Options in Windows 8.1/7.
To show Hidden Files, Folders & Drives on your Windows 11/10 computer:
- Open File Explorer Options
- Click on the View tab
- Locate Hidden Files & Folders
- Select the Show Hidden Files, Folders and Drives option
- Click on Apply and Exit.
You can also open File Explorer Options in Windows 11 as follows:
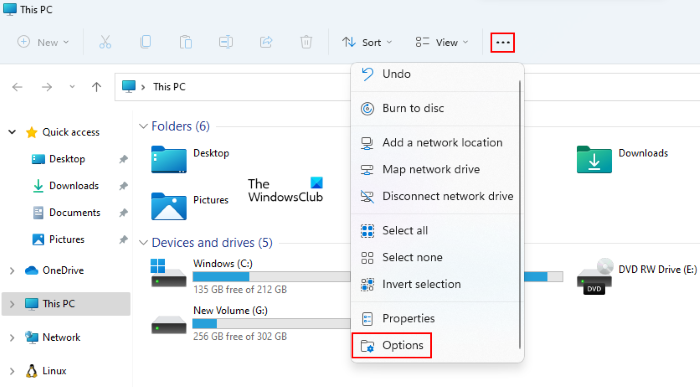
1] Launch File Explorer on Windows 11.
2] Click on the three horizontal dots and select Option. This will open the Folder Options window.
3] In the Folder Options window, click on the View tab and select the radio button that says Show hidden files, folders, and drives.
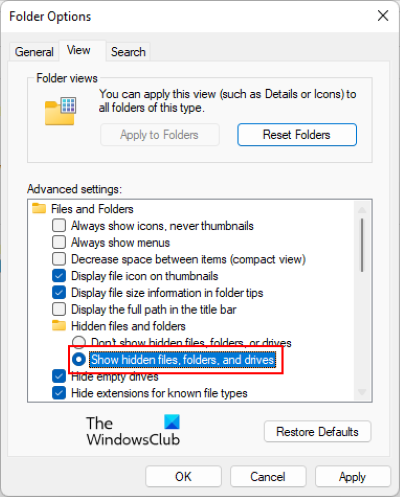
4] Click Apply and then OK.
Alternative method via Explorer Menu bar
In Windows 11, you can open Explorer > View > Show > Select Hidden items.
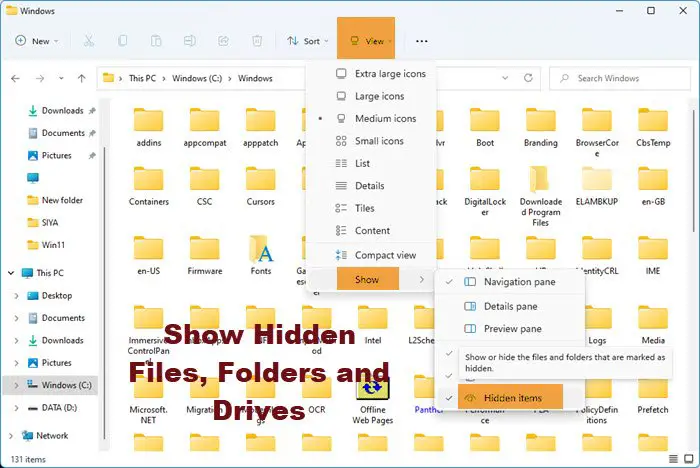
In Windows 10, open Explorer, select the View tab and toggle the Hidden items checkbox to short or hide files and folders.
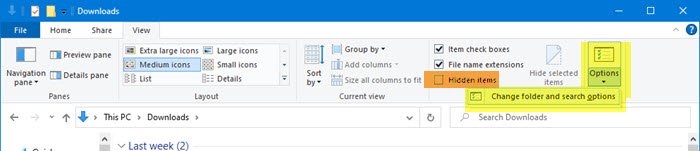
For your information, you can also access the Change folder and search options box from here.
Unhide Protected operating system files
If you wish to unhide and show the Protected operating system files, you need to also uncheck the Hide protected operating system files (Recommended) setting in File Explorer Options, and click Apply.
Show hidden files using Command prompt
The process here is pretty simple. Here are the steps you have to follow:
Open the start command and search for Command Prompt. Select to run it as administrator.
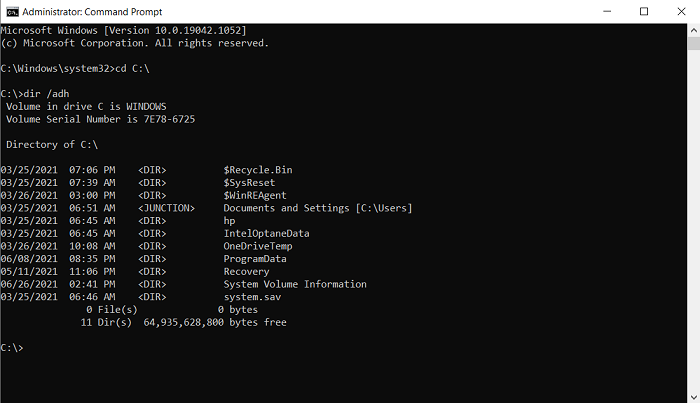
Make a note of the folder in which you want to look for hidden files. For the purposes of this article, we will be using the C:/ drive. Access your drive by using the change directory command cd. Our first command line will look something like
cd C:\
Now, type out the following command line which will show you all the hidden files in the location that you’ve chose
dir /adh
This will show to you all the hidden files, in this case, in the C:/ drive. There are some other keywords that you can use with the dir command if there is some specific information you are looking for. They’re all to be used in a similar manner:
- /a – this will show you only the hidden folders.
- /a:d – this will show you all the directories.
- /a:h – this will show only the hidden files.
- /adh – (The one we’ve used) Gives you all the above information combined.
Let’s now talk about PowerShell and how this process can be replicated there.
Show hidden files using PowerShell
- Open the Start Menu and search for PowerShell, run it as administrator. (You can do the same via the Power User Menu too.)
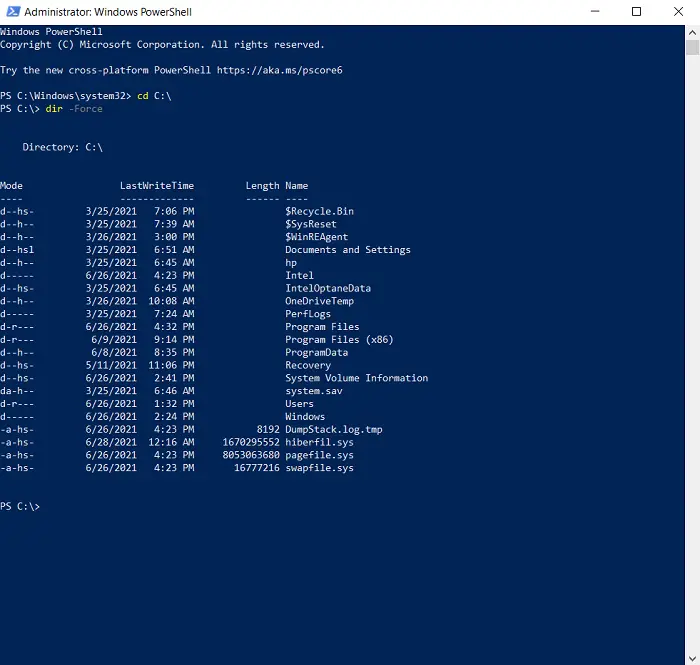
- The process here is quite similar. Access the location of your choice with the change directory keyword cd. It is used the same way as it was in the Command Prompt.
- Once you’re into the location, type the following command line which will display to you all the hidden files inside it.
dir -Force
- You can browse through the hidden files in a folder inside the drive’s root folder by adding that folder’s name to the cd command. Eg., cd C:\Program Files.
- Once you’re inside this particular folder, type/copy the following command and press enter:
Get-ChildItem -Filter *.* -Recurse -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue | where { $_.Attributes -match “Hidden”}
There is a strong chance that the above command line may return a very high number of hidden files and folders, making it impossible for you to actually read through them.
In that case, you can copy the resultant output and have it saved in a text document by modifying the command line. Simply add a >log.txt to the end of the above Get-ChildItem command and all the data will be saved to a text file named log.txt.
TIP: There is another way! You can use attrib.exe to change File Attributes, and/or show the hidden files.
This post will show you how to make a File or Folder Hidden or Read Only.
If you wish to, you can also list all the hidden files & folders on your Windows computer.
BONUS TIP:
- If you find that the Show Hidden Files, Folders and Drives option is missing, then this registry tweak is sure to help you.
- Alternatively, you could use our freeware FixWin to fix this problem. You will find the fix under its Explorer section.
Leave a Reply