By default, Windows uses a minimum of 5% and a maximum of 100% resources to run your apps and the operating system. If you do not want others to play with these settings, you can hide the Minimum and Maximum Processor State in Power Options in Windows 11/10 using Command Prompt and the Registry Editor.

Minimum and Maximum processor states help you decide how much CPU resources you want to be consumed to run Windows OS and installed apps. As we said earlier, 5% is the minimum, and 100% is the maximum resources you can allocate for your operating system and programs. However, it is possible to change this by tweaking the Processor power management settings in the Power Options panel.
If you are using a desktop computer, you have only one option. However, if you are using a laptop, it is possible to show or hide these options for On battery and Plugged in states.
What is Minimum and Maximum Processor State?
The Minimum Processor State refers to the lowest power allocated to the CPU when it’s performing minimal tasks or is inactive. It’s set at 5% by default, which helps conserve battery power during light usage. The Maximum Processor State is, by default, set to 100% for optimal performance.
How to hide Minimum and Maximum processor state in Power Options
To hide Minimum and Maximum processor state in Power Options, follow these steps:
- Open Notepad on your computer.
- Paste the following text.
- Click on File > Save As options.
- Choose a location > select All Files from Save as type > enter a name with .reg file extension.
- Click on the Save button.
- Double-click on the file and click on the Yes option.
To know more about these steps in detail, continue reading.
At first, open Notepad on your computer and paste the following text:
Minimum processor state:
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00 [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Power\PowerSettings\54533251-82be-4824-96c1-47b60b740d00\bc5038f7-23e0-4960-96da-33abaf5935ec] "Attributes"=dword:00000001
Maximum processor state:
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00 [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Power\PowerSettings\54533251-82be-4824-96c1-47b60b740d00\893dee8e-2bef-41e0-89c6-b55d0929964c] "Attributes"=dword:00000001
Click on the File > Save As options and choose a location to save the file.
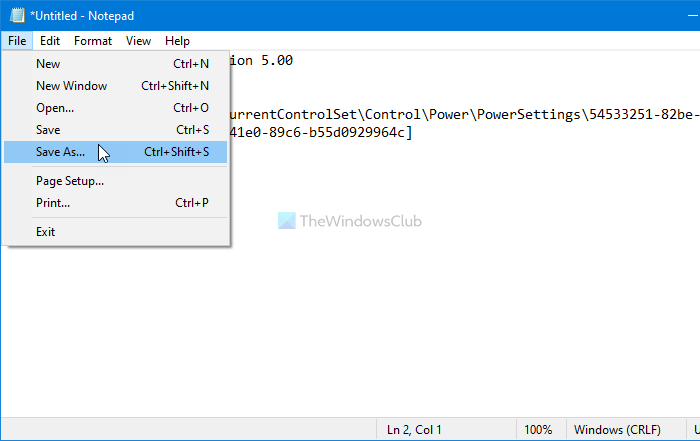
Next, select All Files from the Save as type drop-down list, enter a file with .reg extension, and click on the Save button.
Double-click on the .reg file and click on the Yes option to remove or hide the Minimum or Maximum processor state options from the Power Options panel.
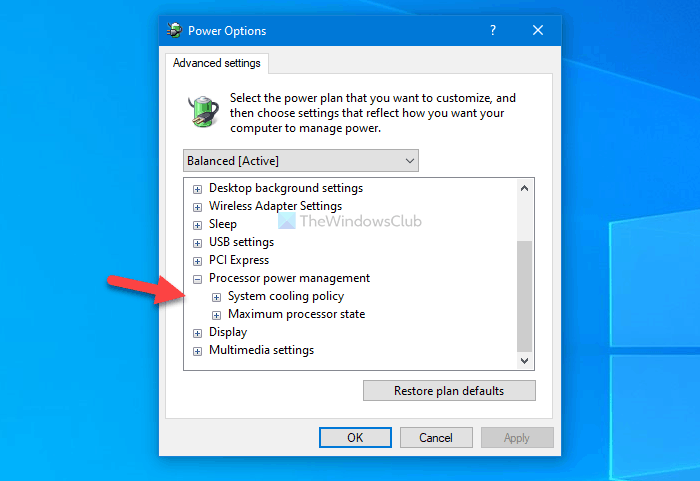
In case you want to show these options, follow this tutorial to open Registry Editor and navigate to these two paths:
Minimum processor state:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Power\PowerSettings\54533251-82be-4824-96c1-47b60b740d00\893dee8e-2bef-41e0-89c6-b55d0929964c
Maximum processor state:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Power\PowerSettings\54533251-82be-4824-96c1-47b60b740d00\bc5038f7-23e0-4960-96da-33abaf5935ec
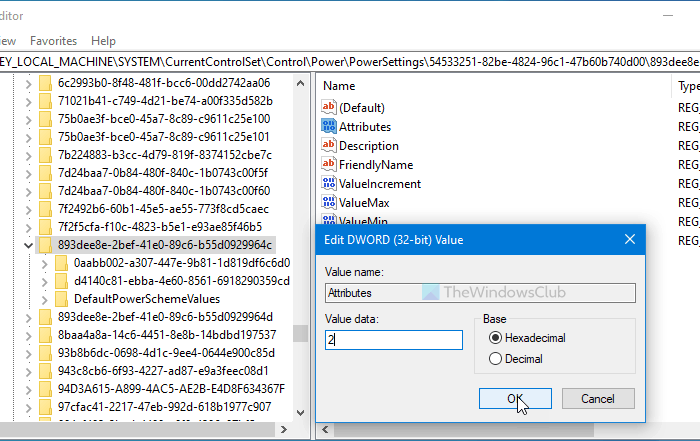
Double-click on the Attributes REG_DOWRD value set the Value data as 2, and click the OK button.
After that, you can re-open the Power Options window to find those two options available.
Tip: Check how much Power your Computer needs.
Add or remove Minimum and Maximum processor state options using Command Prompt
To add or remove Minimum and Maximum processor state options using Command Prompt, follow these steps:
- Search for cmd in the Taskbar search box.
- Click on the Run as administrator and Yes options.
- Enter the powercfg command add or remove these options.
Let’s check out these steps in detail.
It is also possible to show or hide the Minimum and Maximum processor state options using Command Prompt. If you want to follow that method, you have to open Command Prompt with administrator privilege first.
For that, search for cmd in the Taskbar search box and click on the Run as administrator option. Next, you need to select the Yes option in the UAC prompt.
Then, enter the following commands:
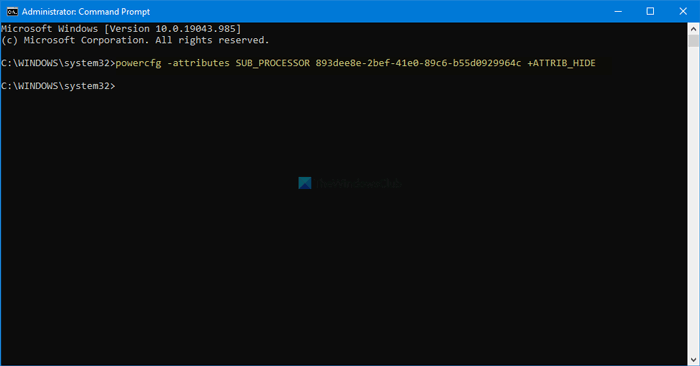
Hide Minimum processor state:
powercfg -attributes SUB_PROCESSOR 893dee8e-2bef-41e0-89c6-b55d0929964c +ATTRIB_HIDE
Hide Maximum processor state:
powercfg -attributes SUB_PROCESSOR bc5038f7-23e0-4960-96da-33abaf5935ec +ATTRIB_HIDE
If you want to show them again, enter these commands:
Show Minimum processor state:
powercfg -attributes SUB_PROCESSOR 893dee8e-2bef-41e0-89c6-b55d0929964c -ATTRIB_HIDE
Show Maximum processor state:
powercfg -attributes SUB_PROCESSOR bc5038f7-23e0-4960-96da-33abaf5935ec -ATTRIB_HIDE
Hope this guide helped.
Read next: How to configure hidden Power Options in Windows 11/10.
Leave a Reply