SLAT or Second Level Address Translation is a technology that works with Hyper-V. It is supported by both Intel and AMD processors. It is called Extended Page Table (EPT) in Intel processors and Rapid Virtualization Indexing (RVI) in the AMD processors. In this post we will see what is SLAT, how to check if the computer supports SLAT and how to enable Second Level Address Translation in BIOS.
Second Level Address Translation (SLAT)
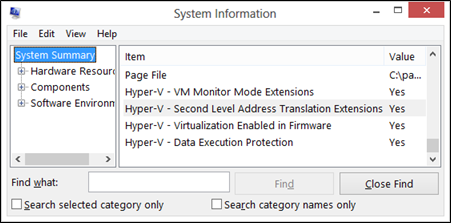
SLAT is supported on Nehalem architecture processors and newer for Intel, and Barcelona processors and newer for AMD.
The special thing about these processors is the fact that they have the Translation Lookaside Buffer or TLB. These processors support Physical memory translation. That type of cache contains all the recently used mappings from the page table of the processors. The built-in cache is used to determine the mapping information by the TLB by a Virtual address needs to be converted to a Physical address. If this data is not found, a page error occurs, and the operating system looks up for the mapping information on the page table. If the relative mapping record is found, it directly goes to be written in the TLB, and the translation of the address takes place.
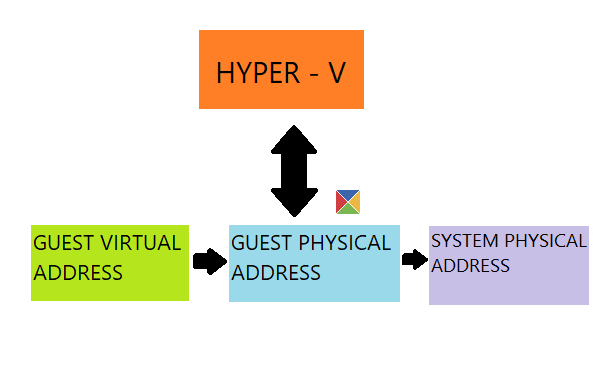
This use of Hyper-V relies more on virtual resources and virtual functions and hence reduces the overhead of the translation of the physical guest address to a real physical address. Hence, a lot of physical resources are saved and can be utilized for other functions.
How to check if the computer supports SLAT
There are two ways by which you can check if your computer supports SLAT:
- Use the CoreInfo utility from Microsoft TechNet.
- Use Turn Windows features on and off utility.
1] Use the CoreInfo utility from Microsoft TechNet
Download the CoreInfo archive from Technet. Extract the contents of the archive in the root of your operating system partition.
Open Windows Command Prompt as an administrator, type in the following command to navigate to the appropriate location:
cd C:\
Next, execute the following command:
coreinfo.exe -v
You will see an output similar to this:
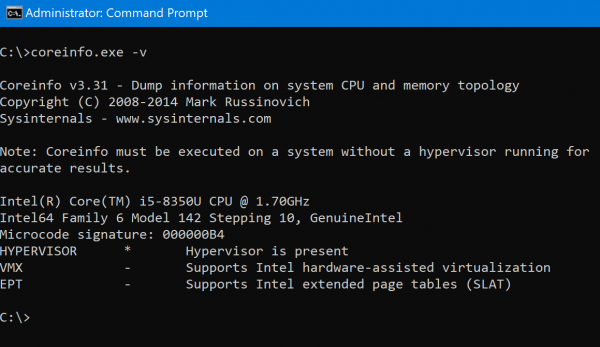
Depending on the processor that you use, you will get an option for EPT or RVI and will have the relevant information about its availability.
2] Turn Windows features on and off
Open the Turn Windows features on and off panel of the Control Panel.
Expand the option for Hyper-V.
If the option for Hyper-V Platform is greyed out, SLAT is not supported.
How to enable SLAT from BIOS
To enable the SLAT feature, you just need to enable Virtualization in your BIOS.
I hope this guide helped you.
Leave a Reply