What is svchost.exe in the Windows 11/10 operating system? Why do I see multiple instances of svchost.exe processes running in my Task Manager? How do I find out basic information, like the name and description for each svchost process? Why is svchost.exe constantly running? Why does my svchost show high Disk or CPU usage? This article will attempt to answer these questions.
What is svchost.exe in Windows 11/10
Svchost stands for Service Host. It is a .exe executable operating system critical file that is located in the System32 folder. When Windows starts up, it checks the Windows Registry and makes a list of Services or groups of Services that it has to load.
The Service Host (svchost.exe) is a shared-service process that serves as a shell for loading services from DLL files.
You, therefore, see multiple such svchost.exe running at the same time. This grouping of services also assists in better control and debugging should the need arise. Services run in svchost are implemented as dynamically linked libraries or dll files.
The svchost.exe process runs with the following parameters or flags:
- When svchost.exe uses the -k flag, a request will be made to the following registry key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Svchost - When svchost.exe uses the -p flag, it enforces different policies: DynamicCodePolicy, BinarySignaturePolicy & ExtensionPolicy
- When svchost.exe uses the -s flag, this will tell the “svchost.exe” process to load only the service specified by the flag from the selected group.
Multiple instances of svchost.exe processes
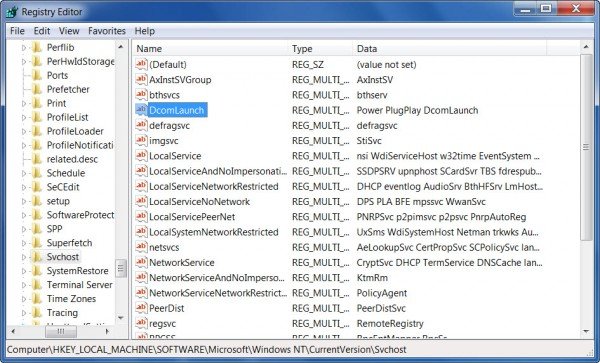
You can see all these svchost.exe groups under the following registry key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\WindowsNT\CurrentVersion\Svchost
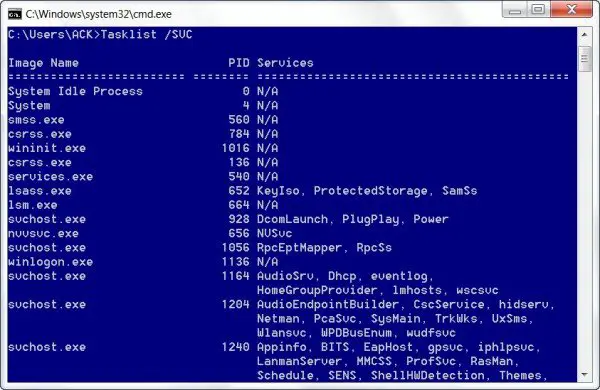
To view the list of services that are running in Svchost, open an instance of the command prompt, type Tasklist /SVC and hit Enter.
svchost.exe high CPU or Disk usage on Windows 11/10
Many times svchost.exe may show high resource utilization. Although it is difficult to isolate the service responsible for this, since many services are associated with this process, the built-in Resource Monitor or SysInternals process Explorer will help you in that direction.
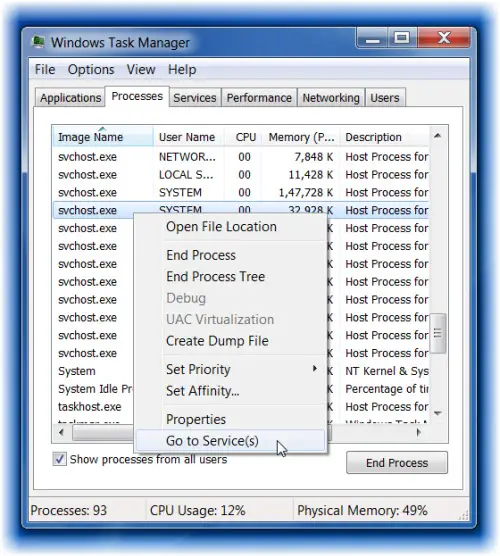
To see which svchost is associated with which single or multiple Service, right-click on the svchost.exe and select Go to Service(s).
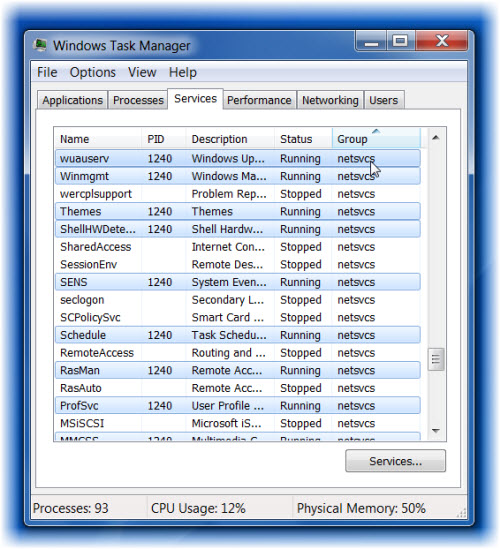
In the Services tab, you will now be able to see the associated services, highlighted.
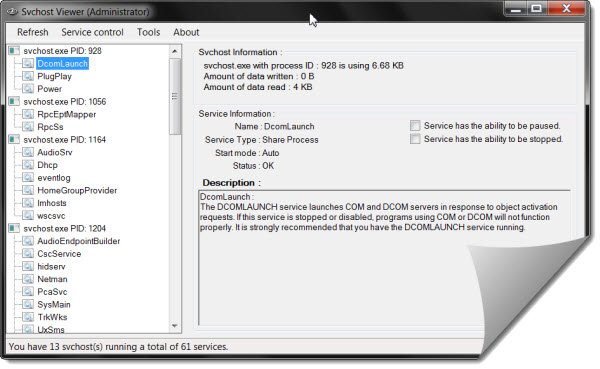
But this does not give you much information. If you need to know more details like the name and description for each svchost process, you can download use freeware portable app Svchost Viewer.
This tool gives you some basic information like the name and description of the services with a particular svchost process. It gives you information like:
- Process ID
- Amount of data written or read
- Name of Service, Service type, Start mode, Status
- Whether the service can be paused or stopped
- A brief description of the Service.
It also lets you stop or pause select services where possible and even lets you access the Service Manager directly.
For instance, Windows Defender is, at times, known to make CPU usage shoot up. Open Windows Defender Security Center > Firewall & Network protection > Disable Firewall for all Networks. Then click on Restore settings and see if that helps.
Read: Service Host: Diagnostic Policy Service 100% Disk Usage.
If you want to reduce the instances of svchost processes, the only way to do it is by reducing the services that start up automatically. If you want to disable services you may want to check out our Windows Services Tweaker. But I advise that you do so, only if you know what you are doing.
How do I know svchost is infected?
Some malware can pretend themselves as genuine files in order to trick antivirus software. Svchost.exe is a genuine file in the Windows operating system. If you want to know whether or not svchost is infected, or whether or not it is a genuine file, you can see its signature. Genuine files are signed by their manufacturers. Open Task Manager and go to the Details tab. Right-click on svchost.exe and click Open file location. Now, right-click on the svchost exe file and select Properties. After that, select the Digital Signatures tab. There you can see the name of the signer. Alternatively, you can also scan the svchost exe file via Windows Defender or your third-party antivirus.
Want to know about these processes?
Shellexperiencehost.exe | RuntimeBroker.exe | TrustedInstaller.exe | Host Process for Windows Tasks | JUCheck.exe.
Leave a Reply