When you log in to a Windows 11/10 domain-joined machine and try to connect to the already mapped drive or multiple client workstations are unable to correctly authenticate to the server and fail with the error message The system cannot contact a domain controller to service the authentication request, then this post intended to help you with solutions to the problem.
The system cannot contact a domain controller to service the authentication request. Please try again later.
This error message usually indicates the client machines can’t reach a domain controller for authentication and almost always points to incorrect DNS settings (DHCP not configured correctly or statically set incorrectly, i.e., mixing DC and non-DC DNS addresses) or routing issues. This typically could be due to the following:
- The domain controller is offline due to maintenance or power outage.
- Network issues if the client device is not correctly configured to establish communication with a domain controller, or if there are issues in the network.
- Host server issues if a domain controller is a virtual machine.
The system cannot contact a domain controller to service the authentication request
If you get the message The system cannot contact a domain controller to service the authentication request in the Enter network credentials dialog when you try to connect or authenticate a client machine to a Windows server machine, then the suggestions presented below can help you resolve the network authentication issue.
- Flush DNS
- Unjoin and rejoin the client machine to the domain
- Additional troubleshooting
Let’s see how these listed suggestions apply to resolving the issue at hand.
Read: An authentication error has occurred (Code: 0x800706be)
1] Flush DNS
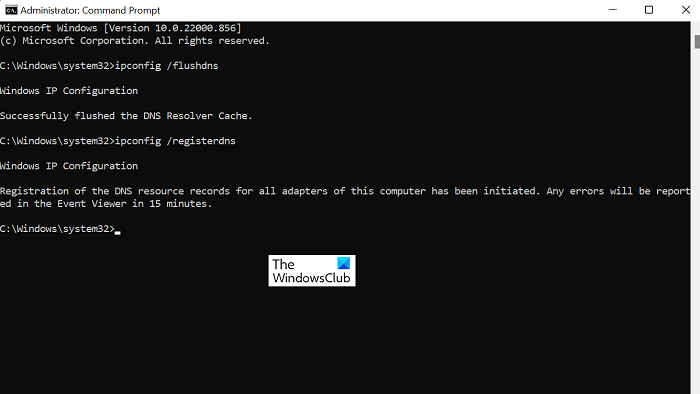
If The system cannot contact a domain controller to service the authentication request error occurs, you can first flush the DNS from the server and client machines, then restart the DNS server Service. Afterward, you can check the Event Logs and make sure no events have been logged.
Read: Your DNS Server might be unavailable in Windows 11/10
2] Unjoin and rejoin the client machine to the domain

There might be several causes why some machines may not be able to authenticate. It could be related to AD token expiration during the time that was not able to authenticate. This solution simply requires that you unjoin and then rejoin the affected client machines to the domain. So, this entails putting the client machines in a workgroup and rebooting, then removing the computers in AD and re-enroll them in the domain. As reported, you may after removing the machine from the domain, resetting the computer account in AD, and trying to rejoin the machine, you may get the following error message:
An Active Directory Domain Controller (AD DC) for the domain could not be contacted.
In this case, if you can successfully ping the domain controller but cannot join the computer, you can refer to the suggestions provided in this guide to resolve the issue.
Read: How to delete Domain Profile in Windows
3] Additional troubleshooting
- If you’re experiencing this issue after resuming from hibernation, take a look at the network connection state by pointing the cursor at the Network icon in the system tray if the appeared tip doesn’t contain your domain name that’s the reason for the error. In this case, you can disable and re-enable the network adapter in Device Manager or unplug it and then plug back the (in 10 seconds) network cord.
- For one reason or another, Windows may have changed the Network Discovery or Sharing profile. In this case, you may have to go to the Network settings and change to a DOMAIN from Public and allow visibility for machines, etc.
- Try pinging the server via computer name and see if the result returns with IPv6. If so, then it’s likely the IPv4 might be getting suppressed and that could cause the issue. In this case, you can try disabling IPv6 and continue with IPv4 and see if that helps.
- Temporarily disable the security software program such as antivirus or firewall (especially from third-party vendors) on your system. Also, if you have VPN software installed and running, see if disabling or disconnecting from the service helps you in this case.
- Check to make sure DNS on your domain controller has the _msdcs.domain.com forward lookup zone and is populated with the various SRV records. Run the dcdiag /e /i /c command on one of your domain controllers and inspect the output and look for DNS issues that may be reported. The tests done by dcdiag include sanity checks to make sure that _msdcs contains precisely the right settings for the domain to work. If not, it will tell you what is missing so you can take the necessary actions.
I hope this helps!
Now read: The specified domain either does not exist or could not be contacted
How do I troubleshoot AD authentication problems?
If you are having AD authentication problems, as part of the process of troubleshooting Active Directory you can do the following:
- Run diagnostics on domain controllers.
- Test DNS for signs of trouble.
- Run checks on Kerberos.
- Examine the domain controllers.
Active Directory uses Kerberos to authenticate communication on the domain. Therefore, your AD server must accept this authentication type as well. If Kerberos stops working, then the authentication process breaks down.
How do I force Domain Controller authentication?
To force a client to validate its logon against a specific domain controller, do the following:
- Open Registry Editor.
- Navigate to the path below:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\NetBT\Parameters
- Create a New > DWORD value with the name NodeType and press ENTER.
- Double-click on the new value and set it to 4 (this sets the network to an M-mode/mixed which means it will perform a broadcast before querying name servers for resolution). By default, a system is 1 if no WINS servers are configured (B-node/broadcast) or 8 if at least one WINS server is configured (H-node/queries name resolution first then broadcasts).
- Next, create (if it does not exist) a New > DWORD with the name EnableLMHOSTS value and set its value to 1.
- Close the registry editor.
- Reboot the machine.