If the Task Manager is not showing network usage on your Windows 11/10 PC, read this post to learn how to troubleshoot the issue. Network usage refers to the amount of data being sent and received by a computer over the network. This includes data from internet browsing, uploads, downloads, and other network activities performed by various applications or system processes.
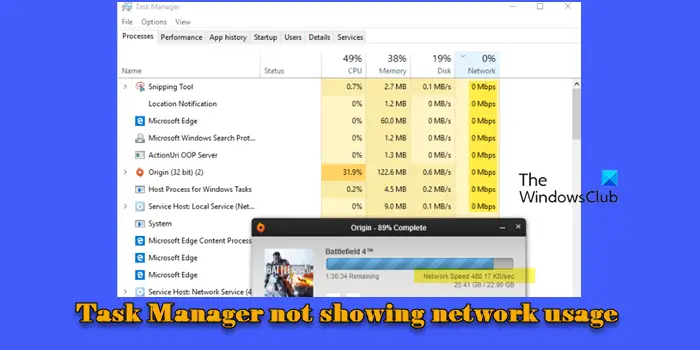
Task Manager helps you monitor network usage by displaying real-time data transfer rates for each application and process running on the system. However, sometimes, it may not show the network usage or keeps displaying 0% for all apps and processes. If this is the case with you, we will show you several potential solutions to troubleshoot the issue.
How to show Network usage in Task Manager?
If the Task Manager is not showing network usage on your Windows 11/10 PC, ensure the Network column is visible in the Processes tab. Right-click on the column headers under the Processes tab and ensure ‘Network’ is checked in the list of options. The tab shows real-time network speeds (with a slight delay) and if there’s no high-load network activity on your system, it may show a speed of ‘0 Mbps’ for all apps. Also, if you have Gigabit Ethernet, the percentage up to 1 decimal place would be zero. So, if the resource values are set to show ‘percent,’ you may end up with all apps showing 0.0%.
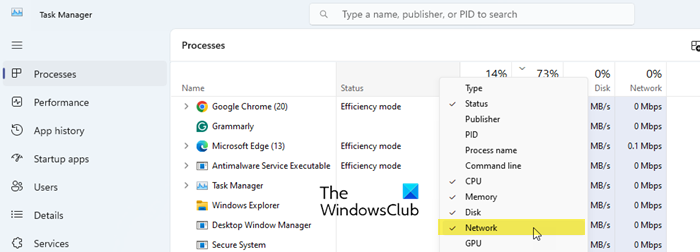
Task Manager not showing Network usage in Windows 11
If your Task Manager is not showing the actual network usage but keeps displaying 0% despite data going in and out, one of these fixes is sure to help you:
- Check the Update Speed option
- Uninstall any third-party Network Monitoring software
- Disable conflicting drivers
- Activate the Windows NDU
- Run Network and Internet Troubleshooter
- Reinstall Network adapter driver
- Check for Windows Update
Let us see this in detail.
1] Check the Update Speed option
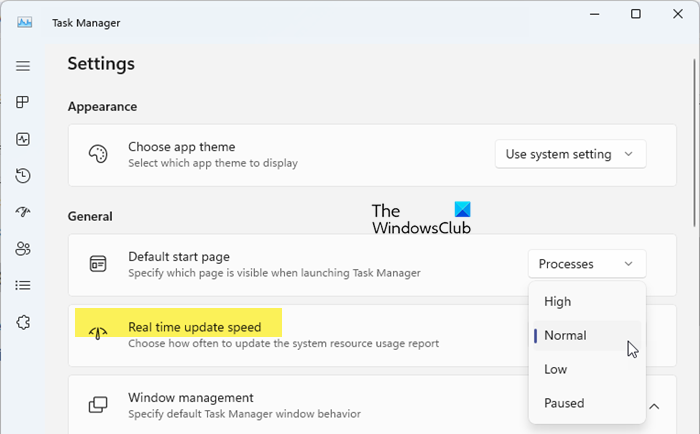
The Task Manager may not show network usage if the Real time update speed is Paused in Task Manager settings. The ‘Real time update speed’ option allows you to choose how often to update the system resource usage report in Task Manager. This includes network usage as well.
To fix this, click the Settings (gear) icon in the bottom-left corner of the Task Manager window and set Real time update speed to Normal.
2] Uninstall any third-party Network Monitoring software
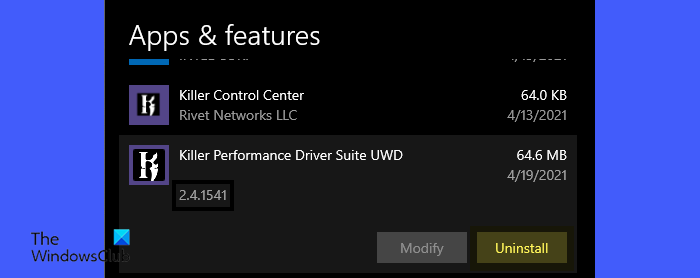
Killer Networking suite or similar network management or network optimization software include network filtering drivers that prioritize network traffic and manage bandwidth. These drivers can conflict with the Task Manager’s ability to read network usage data, causing it to show a 0% value for all apps and processes.
To fix this, try disabling any third-party Network Monitoring software you may have installed recently and see if the issue resolves. If it does, consider uninstalling the software.
3] Disable conflicting drivers
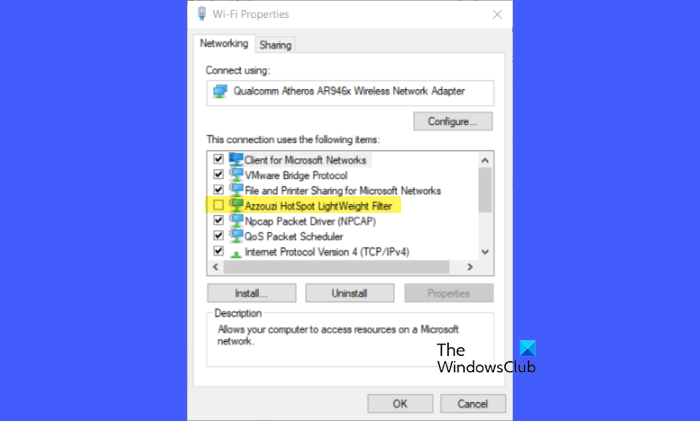
Drivers like Network Lightweight Filter (NWF) or Network Filter Driver are used along with other network drivers to manage network traffic in Windows. They are typically installed by network management or optimization software to provide additional functionalities like bandwidth management or network diagnostics.
Conflicts between third-party network drivers and the native Windows network drivers can prevent accurate network usage reporting in Task Manager. If you do not prefer uninstalling the underlying software, temporarily disable the filter drivers and see if it resolves the issue.
Open Control Panel. Go to Network and Internet > Network and Sharing Center. Click on your network and select Properties in the Network Status window. Go through the list under ‘This connection uses the following items‘ and uncheck any third-party network filter drivers.
Please note that the conflicting software might not work properly until you re-enable its drivers.
4] Activate the Windows NDU
NDU stands for Network Data Usage. It is a Windows system driver that monitors and collects network usage data, which is used by various Windows features, including Task Manager, to display network activity and usage statistics.
In a standard Windows installation, the NDU driver is usually enabled, and network usage statistics are tracked by default. However, some network management or optimization software (like Killer Networking Suite) or security software (antiviruses) might disable the NDU driver to prevent potential vulnerabilities or conflicts.
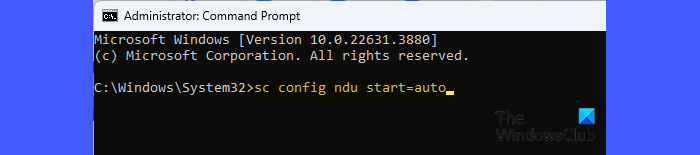
To fix this, re-activate the Windows NDU by executing the following command in an elevated Command Prompt:
sc config ndu start=auto
Reboot your PC.
After this, the Task Manager Processes tab should show traffic in the Network column, but the conflicting software might not work properly. So it would help if you uninstalled the software (as suggested above) or disabled Windows NDU to make it display network bandwidth correctly.
The command to disable Windows NDU is as follows:
sc config ndu start=disabled
5] Run Network and Internet Troubleshooter
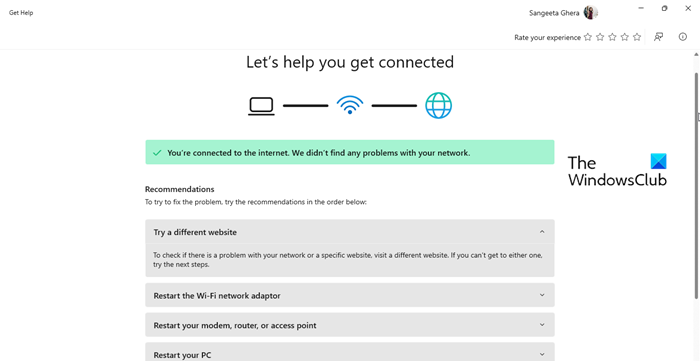
Next, try running the Get Help Network and Internet Troubleshooter. The troubleshooter scans for common issues with network adapters, connection settings, and related components. It may fix problems with network services that are necessary for monitoring and reporting network usage in the Task Manager.
6] Reinstall Network adapter driver
Driver-related issues can affect network monitoring, causing the Task Manager to display incorrect network utilization statistics. Reinstalling the driver forces Windows to reset and reload the network adapter’s functionality, which may resolve issues related to network monitoring.
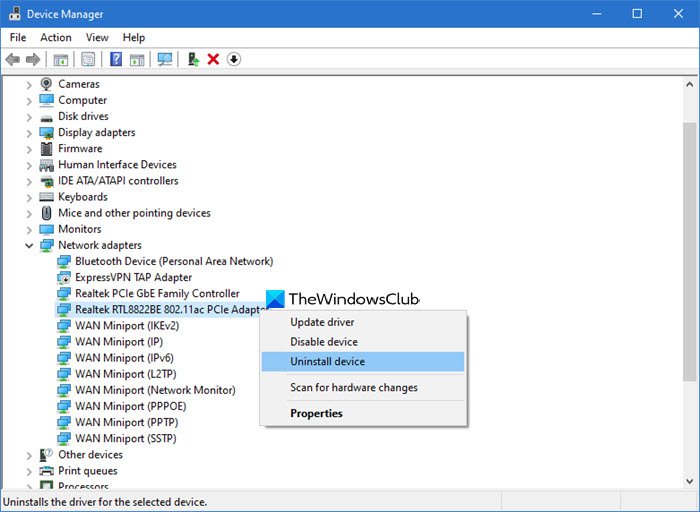
- Press Win + X and select Device Manager.
- Expand Network adapters.
- Right-click your network adapter and select Uninstall device.
- Check ‘Delete the driver software for this device‘ and click Uninstall.
- Reboot the PC and allow Windows to automatically reinstall the default driver for your Wi-Fi or Ethernet adapter.
To manually install the updated driver, download the latest Network driver from the manufacturer’s website, run the installer, and follow the on-screen instructions.
7] Check for Windows Update
If all else fails, check for any pending Windows updates and install them. Go to Settings > Windows Update > Check for updates). This has worked for a few users in resolving the issue.
I hope the above solutions will help fix your Task Manager’s glitch in showing the actual network usage of your system’s apps and services.
Tip: To check the overall network speed, switch to the Performance tab and select the Ethernet or Wi-Fi option. To view detailed real-time data on network activity for individual processes and services, click the three-dot icon in the top-right corner of the Performance screen and select Resource Monitor.
Read: Fix Service Host Network Service High network usage in Windows.
How do I show network status on Taskbar?
Press Win + I to open the Settings app. Navigate to Personalization > Taskbar. Under the Taskbar items section, make sure Network is toggled On. If the network icon is not visible in the system tray, click on the Up Arrow (or Show hidden icons) to see additional icons. If the network status icon is still not showing, you might need to restart Windows Explorer and reinstall your network adapter driver.
Read Next: Limit, Monitor, and Manage Monthly Internet Data Usage in Windows.
Leave a Reply