Thunderbolt is the hardware brand interface developed by Intel. It acts as an interface between computer and external devices. While most of the Windows computers come with all sorts of ports, many companies use Thunderbolt to connect to various types of devices. It makes connecting easy, but according to research at the Eindhoven University of Technology, the security behind Thunderbolt can be breached using a technique — Thunderspy. In this post, we will share tips you can follow to protect your computer against Thunderspy.
What is Tunderspy? How does it work?
Its a stealth attack that allows an attacker to access direct memory access (DMA) functionality to compromise devices. The biggest problem is that there is no trace left as it works without deploying any mind of malware or link bait. It can bypass the best security practices and lock the computer. So how does it work? The attacker needs direct access to the computer. According to the research, it takes less than5 minutes with the right tools.
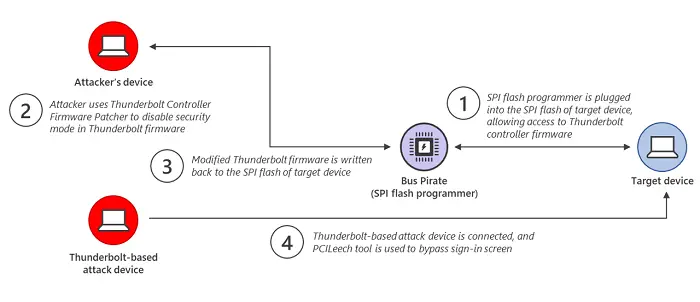
The attacker copies the Thunderbolt Controller Firmware of the source device to his device. It then uses a firmware patcher (TCFP) to disable the security mode enforced in the Thunderbolt firmware. The modified version is copied back to the target computer using the Bus Pirate device. Then a Thunderbolt-based attack device is connected to the device being attacked. It then uses the PCILeech tool to load a kernel module that bypasses the Windows sign-in screen.
So even if the computer has security features like Secure Boot, strong BIOS, and operating system account passwords, and enabled full disk encryption, enabled, it will still bypass everything.
TIP: Spycheck will check if your PC is vulnerable to the Thunderspy attack.
Tips to protect against Thunderspy
Microsoft recommends three ways to protect against the modern threat. Some of these features that are built into Windows can be leveraged while some should be enabled to mitigate the attacks.
- Secured-core PC protections
- Kernel DMA protection
- Hypervisor-protected code integrity (HVCI)
That said, all this is possible on a Secured-core PC. You simply cannot apply this on a regular PC because the hardware is not available that can secure it from the attack. The best way to find out if your PC supports it is by checking the Devic Security section of the Windows Security app.
1] Secured-core PC protections
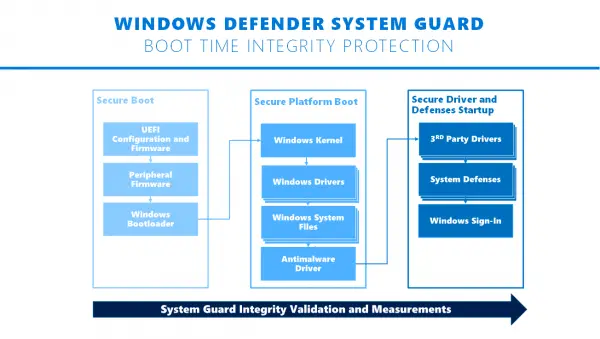
Windows Security, Microsoft’s in-house security software, offers Windows Defender System Guard and virtualization-based security. However, you need a device that uses Secured-core PCs. It uses rooted hardware security in the modern CPU to launch the system into a trusted state. It helps mitigate attempts made by malware at the firmware level.
2] Kernel DMA protection
Introduced in Windows 10 v1803, Kernel DMA protection makes sure to block external peripherals from Direct Memory Access (DMA) attacks using PCI hotplug devices such as Thunderbolt. It means if someone tries to copy malicious Thunderbolt firmware to a machine, it will be blocked over the Thunderbolt port. However, if the user has the username and password, he will be able to bypass it.
3] Hardening protection with Hypervisor-protected code integrity (HVCI)
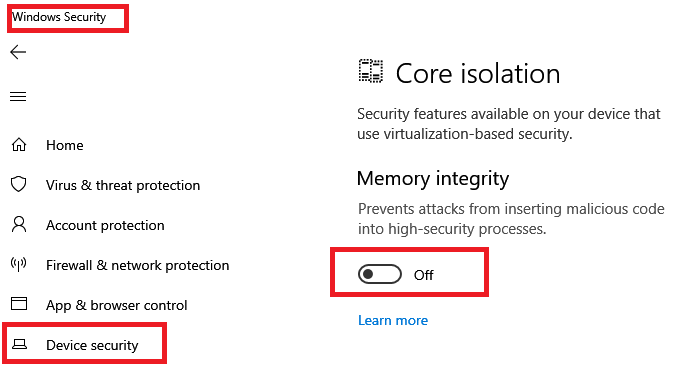
Hypervisor-protected code integrity or HVCI should be enabled on Windows 10. It isolates the code integrity subsystem and verified that there Kernel code is not verified and signed by Microsoft. It also ensures that kernel code cannot be both writable and executable to make sure unverified code does not execute.
Thunderspy uses the PCILeech tool to load a kernel module that bypasses the Windows sign-in screen. Using HVCI will make sure to prevent this as it will not allow it to execute the code.
Security should always be at the top when it comes to buying computers. If you deal with data that is important, especially with business, it is recommended to purchase Secured-core PC devices. Here is the official page of such devices on the Microsoft website.
Leave a Reply