Windows 11 is right around the corner, and Microsoft made sure to include security requirements for anyone who wants to upgrade. This means millions of Windows 10 users will have to purchase new computers to experience what the new operating systems have to offer.
Your computer will need to support Trusted Platform Module (TPM 2.0). However, from a hardware standpoint, only the 8th generation and up from the Intel side of things support TPM 2.0. As for AMD, only Zen 3 and up.
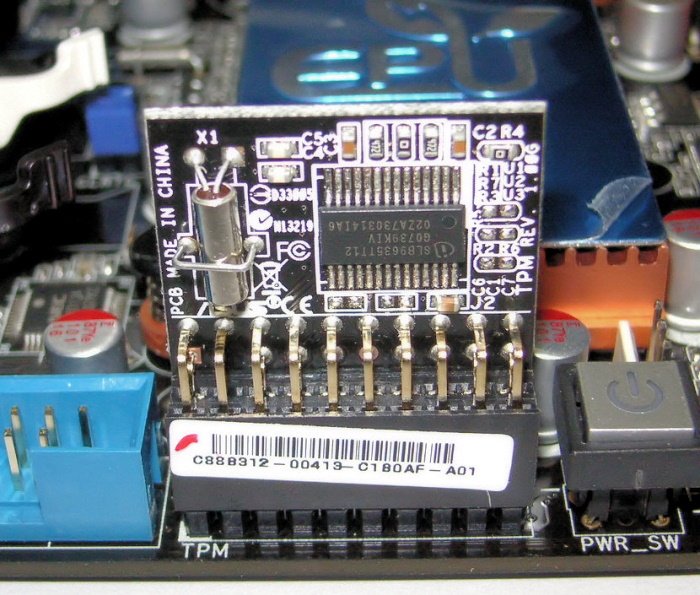
If you want to learn more, please read our post on Chipsets and motherboards that support Windows 11 to get a deeper understanding of the type of hardware required.
What is TPM (Trusted Platform Module)?
Trusted Platform Module or TPM is a specialized and dedicated chip that stores cryptographic keys. It acts as endpoint security for the devices which support it.
When it comes down to storing encryption keys on the hardware stage, that is where TPM comes into play. Many security researchers believe it is best to store security keys from a hardware level instead of software to keep hackers at bay better. The entire tech industry is adopting TPM, and as such, Microsoft does not want to be left behind, especially seeing as we are now knee-deep in the digital age.
What is PTT (Platform Trust Technology)?
PTT offers the capabilities of discrete TPM 2.0. Intel PTT is a platform functionality for credential storage and key management used by Windows 11/10. We should point out that PTT is an Intel technology.
Difference between TPM and PTT
Platform Trust Technology is designed to work with Trusted Platform Module, so there are no real vs. since they do not work to accomplish the same overall task. We explain a bit more below.
Platform Trust Technology vs. Trusted Platform Module
To begin, we should point out that PTT and TPM are different technologies, but they complement each other. You see, PTT is there if your computer supports TPM 2.0, but it does not contain a dedicated chip. We know this because many CPUs have TPM support from a firmware level.
Intel created PTT to help with enabling TPM on computers that do not have dedicated support, and from what we can tell, it works quite fine. The technology was created back in 2013; therefore, we expect computers with at least the 4th generation Intel CPUs to run Windows 11 via PTT. At least, we are making this point based on a theory since we haven’t tested it ourselves.
So, what about AMD? Well, we have learned that Zen CPUs come packed with an alternative to PTT known as fTPM.
Related: How to clear and update TPM firmware.
Does your computer support TPM?
From what we have gathered, computers after 2015 should support TPM even if they do not have a dedicated chip installed. Now, this is where PTT comes into play. Intel added this technology into computers starting from their 4th generation chips.
With this technology, more people might get the chance to download and install Windows 11 than previously thought.
Read: How to enable AMD CPU fTPM in BIOS?
How to tell if your computer supports TPM 2.0
There are multiple ways to check TPM chip availability. However, you should know that it should be enabled at the hardware level so that security software security like Bitllocker can use it.
- Using TPM Management
- Enable it in BIOS or UEFI
- Using the Security Node in Device Manager
- Using WMIC command.
You can use TPM Diagnostics Tool in Windows 11 to find out the Trusted Platform Module chip information of your system.
Leave a Reply