Windows Server offers tons of tools for admins in case an application or computer is not able to connect to a specific port or server IP. One thing that instantly pops up is using tools to resolve DNS and other network issues, but if you love using PowerShell, there is a brilliant command Test-NetConnection that you can use.
Troubleshoot Network connectivity issues via PowerShell
You can use the Test-NetConnection cmdlet to find out diagnostic information for a connection. It includes support for the Ping test, TCP test, route tracing, and also route selection diagnostics.
Depending on which options are used, the output will consist of information such as ComputerName, RemoteAddress, SelectedSourceAddress, OutgoingInterfaceIndex, SelectedNetRoute, and more.
Here is the list of supported parameters
- CommonTCPPort: Specifies the typical service TCP port number
- ComputerName: Specifies the Domain Name System (DNS) name or IP address of the target computer.
- ConstrainInterface: Specifies the interface constraint to use for route diagnostics.
- ConstrainSourceAddress: Specifies the source address constraint to use for route diagnostics.
- DiagnoseRouting: Indicates that route diagnostics run to output the route and source address selection information for the remote host.
- Hops: Specifies the number of hops to traverse in a traceroute command.
- InformationLevel: Specifies the information level Detailed or Quiet
- Port: Specifies the TCP port number on the remote computer.
- TraceRoute: Indicates that Tracert runs to test connectivity to the remote host.
Using the powerful Test-NetConnection cmdlet
Test-NetConnection -ComputerName "www.contoso.com" -ConstrainInterface 5 -DiagnoseRouting -InformationLevel "Detailed" ComputerName : www.contoso.com RemoteAddress : 2600:1409:a:185::2768 ConstrainInterfaceIndex : 5 SelectedSourceAddress : 2001:4898:e0:79:75dd:64cf:d9ff:f86 OutgoingInterfaceIndex : 5 SelectedNetRoute : DestinationPrefix: ::/0 NextHop: fe80::200:5eff:fe00:202 RouteSelectionEvents : IP: Route [DestinationPrefix: ::/0 NextHop: fe80::200:5eff:fe00:202 InterfaceIndex: 4 RouteMetric: 256] is blocked for Destination: 2600:1409:a:185::2768 ConstrainInterfaceIndex: 5 ConstrainScopeZone: 1 in Compartment: 1, Reason: InterfaceConstraint. SourceAddressSelectionEvents : IP: Source address 2001:4898:e0:79:75dd:64cf:d9ff:f86 is preferred over fe80::75dd:64cf:d9ff:f86 for destination 2600:1409:a:185::2768 Rule = 2.0. IP: Source address 2001:4898:e0:79:75dd:64cf:d9ff:f86 is preferred over fe80::75dd:64cf:d9ff:f86 for destination 2600:1409:a:185::2768 Rule = 2.0. RouteDiagnosticsSucceeded : True
List of Sample Commands
Here are a few sample commands you can try on your computer. Some of these commands will need admin privileges, so make sure to launch PowerShell 7 or PowerShell 5.1 with the required permission.
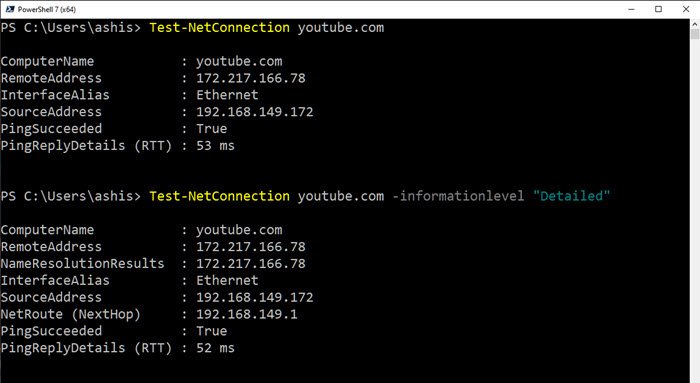
Test-NetConnection youtube.com
More detailed information on the connectivity:
Test-NetConnection youtube.com -InformationLevel "Detailed"
When working with web services, it is to test a specific TCP port.
Test-NetConnection youtube.com -Port 443 -InformationLevel "Detailed"
Perform route diagnostics to connect to a remote host.
Test-NetConnection -ComputerName itopstalk.com -DiagnoseRouting -InformationLevel Detailed
Find the default port of a website
Test-NetConnection -ComputerName microsoft.com -CommonTCPPort HTTP
Run Trace Route for a website
Test-NetConnection -ComputerName google.com -TraceRoute
That said, it is beneficial if you are on a non-windows platform but uses the same command as in Windows.
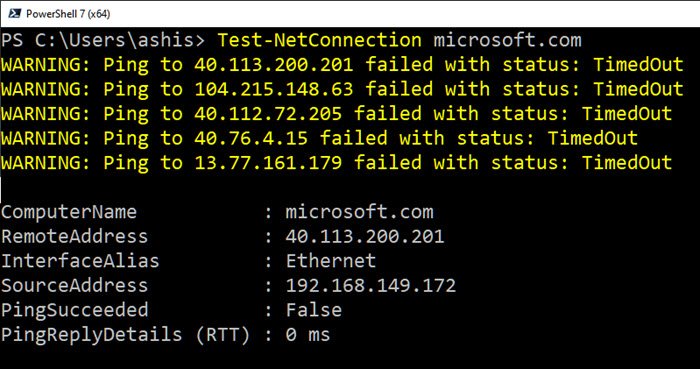
Apart from this, I have also noticed executing commands for some websites like Microsoft.com. It doesn’t work. Ping fails all the time, which could be a server thing blocking such random requests.
Leave a Reply