Many a time Windows Updates fail to install when your PC hardware is not compatible with the software update. This is usually based on issues Microsoft knows, and the feedback it gets from OEM and Windows Insiders. Windows Update comes with its own kill switch built into the KB patches or any update which triggers in case of hardware compatibility issues. Today, we are talking about how to block the unsupported hardware popup in Windows Update.
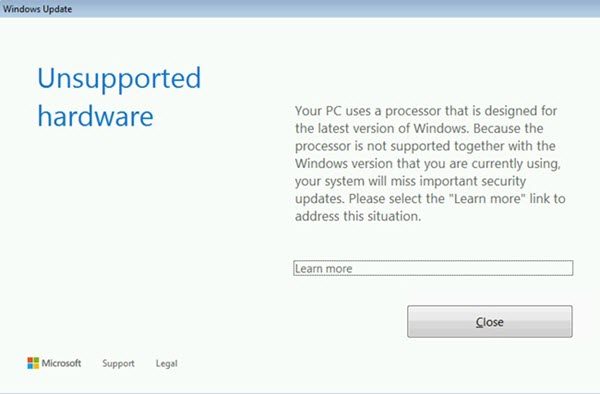
This issue has majorly popped up for Windows 7 and Windows 8.1 machines which were due upgrading to Windows 10. It triggered this kill switch for Intel 7th generation processors, including Sky Lake and Kaby lake architecture, and the AMD Ryzen processor line. Because of this, no more updates were rolling out for these PCs.
Fix: The processor is not supported together with the Windows version that you are currently using message.
Block Unsupported Hardware Popup
If you are up for the risk to install the update, and sure that it will work for you, here is a tool to fix this. Zeffy, a developer, on GitHub has created a tool WUFUC, which scans for these type of kill switches, and patches. This way the update can be installed on those PC. This guy has reversed engineer Windows Update.DLL to remove the flag.
- Download the file from here.
- Extract the file on your computer, and then right-click on the batch file called as “aio-wuaueng.dll-patch_xxx“.
- Run this file as Administrator
- You may also choose to use the installer program if you feel comfortable. There is a 32 Bit, and a 64-bit version available.
This will patch the DLL with its own settings. Reboot the computer, and then re-attempt to download Windows Update again. It should work now.
A few things you should know:
- Every time a Windows Update completes, the DLL gets restored to the official version. You will have to reinstall the patch if that happens every time.
- The sfc /scannow fails because of this patch. Make sure to take backups of your computer using disk image tools.
- Removing Microsoft KB4015549 update multiple times, and rebooting the PC sometimes work as well. However, it’s not guaranteed.
So basically every time Microsoft releases an update, download the latest version of the tool from GitHub, and use it before installing it on your PC.
However, I would suggest you try the regular update and see if it works for you. It is possible that Microsoft might have fixed or rolled out a solution for you.