Windows PowerShell is a powerful utility that comes preinstalled on Windows 11/10. Microsoft has been pushing it hard to become useful for developers and IT professionals. Windows PowerShell can also be used to manage Hard Drives and SSDs. In this post, we will check how to use PowerShell to find information about any class of hard drive.
Use PowerShell to get physical Disk information
There are two things that you can do using PowerShell to get physical disk information, including serial number, disk size, free space, and more.
- Get General Information.
- Retrieve detailed information.
The command works with all the storage devices connected to your computer. You can identify the type of device by looking at the Device type column. The column displays an integer that corresponds to the type of disk drive the logical disk represents.
- 0 – Unknown.
- 1 – No Root directory.
- 2 – Removable Disk.
- 3 – Local Disk.
- 4 – Network Drive.
- 5 – Compact Disc.
- 6 – RAM Disk.
1] Get General Information
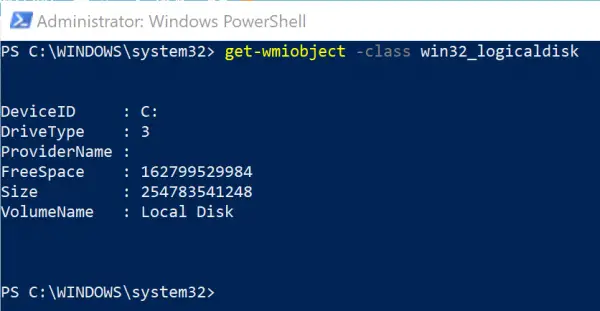
Open Windows PowerShell and execute the following command to get general information about the connected hard drives:
get-wmiobject -class win32_logicaldisk
The results will display DeviceID, DriveType, ProviderName, FreeSpace, Size, VolumeName.
2] Retrieve detailed information
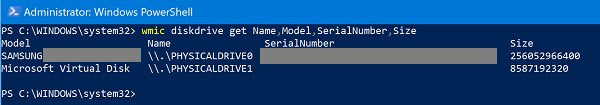
Open Windows PowerShell once again, and type in the following code and hit Enter:
wmic diskdrive get <PARAMETERS>
The following are the parameters, and in case of multiple parameters, they should be separated by a comma:
- Availability
- BytesPerSector
- Capabilities
- CapabilityDescriptions
- Caption
- CompressionMethod
- ConfigManagerErrorCode
- ConfigManagerUserConfig
- CreationClassName
- DefaultBlockSize
- Description
- DeviceID
- ErrorCleared
- ErrorDescription
- ErrorMethodology
- FirmwareRevision
- Index
- InstallDate
- InterfaceType
- LastErrorCode
- Manufacturer
- MaxBlockSize
- MaxMediaSize
- MediaLoaded
- MediaType
- MinBlockSize
- Model
- Name
- NeedsCleaning
- NumberOfMediaSupported
- Partitions
- PNPDeviceID
- PowerManagementCapabilities
- PowerManagementSupported
- SCSIBus
- SCSILogicalUnit
- SCSIPort
- SCSITargetId
- SectorsPerTrack
- SerialNumber
- Signature
- Size
- Status
- StatusInfo
- SystemCreationClassName
- SystemName
- TotalCylinders
- TotalHeads
- TotalSectors
- TotalTracks
- TracksPerCylinder
The result will be sorted, a tabular form of the requested data inside the Windows PowerShell command line.
You can read more about the commands on learn.microsoft.com.
Read next: List Hard Drives using Command Prompt & PowerShell.
Leave a Reply