The Command Prompt is command-line utility that comes out of the box on Windows 11/10. But for those who know its true potential, it is a great replacement for many of the users’ third-party software. For example, it can help you organize your hard drive partitions, create a bootable USB drive for you, refresh all the BIOS files, and much more. Many administrators and power users tend to make use of multiple commands on this command line to get their work done. Today, we will be talking about methods that will help the user view their Command Prompt history and save that Command Prompt history on Windows 11/10.
View, save, clear Command Prompt command History
We will cover the following topics:
- View using DOSKEY.
- View using the F7 key.
- Save the Command Prompt History.
- Clear command prompt history.
1] View CMD command history using DOSKEY
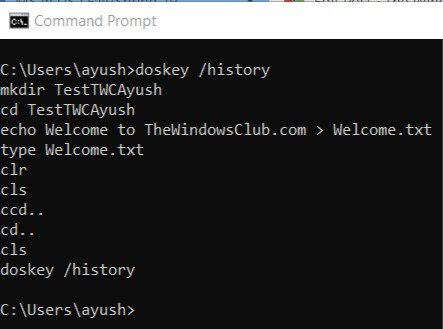
This method is a pretty straightforward one. After you have entered a series of commands in the Command Prompt window, all you need to do is enter the following command inside the same Command Prompt window-
doskey /history
After that, you will be able to check all the commands that you just entered during that session in the Command Prompt in the same sequence as you entered it.
You can check a screen snippet of the same above.
Read: How to clear CMD screen?
2] View CMD history using the F7 key
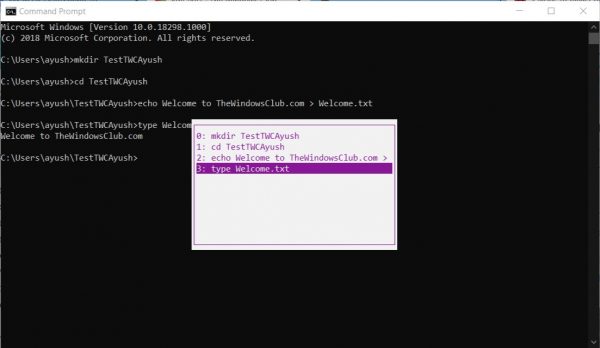
This is better than the DOSKEY method mentioned above. I am not claiming that because this is better, but if you just want to get back to any previously executed command, it is really reliable.
To view the command history, you need to hit the F7 key. F7 works for Command Prompt and PowerShell as well.
This will lead to a small pop-up to appear with the list of all the previously executed commands in the session.
You can use the up and down arrow key to navigate through the list and hit the Enter key to select any of them.
2] Save the Command Prompt History
Sometimes, you might need to keep a record of the commands they used in a session using the Command Prompt in a TXT, HTML, CSV or a RTF file.
For that, you can use an extension of the DOSKEY command.
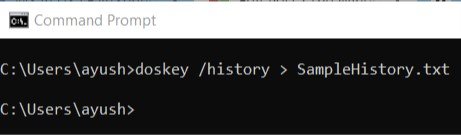
You just need to enter the following command and then hit the Enter key,
doskey /HISTORY > SampleHistory.txt
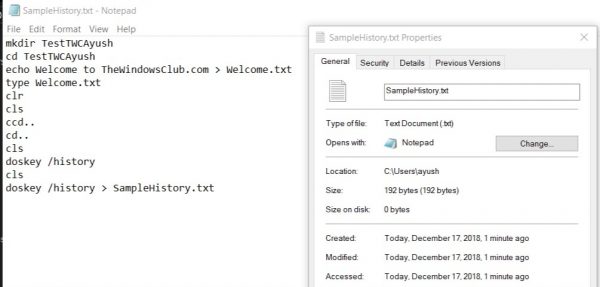
Then, your backed-up history file will be saved in a location where you executed the command in the Command Prompt window.
4] Clear command prompt history using Alt+F7
The simplest way is to restart the Command Prompt. The command history is cleared automatically every time you close it and start the command prompt again.
To clear the command history, you can also use Alt+F7 keyboard shortcut. Alt+F7 works for Command Prompt and PowerShell as well.
You can also delete the command history by using the Registry Editor. Navigate to the following key:
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\RunMRU
Next, select RunMRU and erase all the values having a name, a letter of the alphabet in the right pane. After this, right-click on MRUList > Edit, and delete the contents of Value data.
TIP: More Command Prompt tips & tricks here.
How to view command history in Windows PowerShell?
Like Command Prompt, Windows PowerShell also keeps a history of commands executed by you. Open PowerShell in Windows 11/10 and execute the following command:
Get-History
If you want, you can get more information for each command (command ID, execution status, command line, start execution time, and end execution time). For this, use the command given below:
Get-History | Format-List -Property *
How to export command history in PowerShell?
You can export or save the command history of PowerShell as a CSV file to your desktop or any location on your Windows 11/10 system. For this, you need to use the Export-CSV cmdlet, the path for the output file and file format. The command would be:
Get-History | Export-CSV C:\Users\Username\Desktop\CommandHistory.CSV
Replace Username with the actual username, the Desktop with the location or folder where you want to save the output, and CommandHistory with the file name of your choice.
Read next: How to clear Run command history in Windows.