Cyber Security is a branch of Technology that protects computer systems, mobile devices, servers, etc., from malicious attacks. Various malicious actors perform these malicious attacks. The purpose of malicious actors is to access or destroy users’ sensitive information. Security software protects users from cyber threats. Antivirus software is the most widely used Security software. False Positive term is most commonly used in the field of Cyber Security. In this article, we will talk about what a False Positive in Cyber Security is.

What is a False Positive in Cyber Security?
False Negative and False Positive are the most commonly used terms in the field of Cyber Security. Some of you might have heard these terms. This post discusses what are False Positives and False Negatives detected by antivirus & security software and how you can whitelist such detections.
A False Positive is a false alarm generated by antivirus or other security software. In simple words, when an antivirus or Security Software considers a genuine file or program malicious, it is called a False Positive flag.
If you have installed antivirus software on your system, you might have experienced an issue where your antivirus software blocked a genuine file or program. In this case, the blocked program does not function properly or refuses to launch. False Positive flags are always incorrect.
How does a False Positive occur?
Antivirus software works on different methods. These methods include Signature-based malware detection, Behavior-based malware detection, etc. In the Signature-based malware detection technique, antivirus software uses the signatures to identify whether a file or a program is genuine or malicious. These signatures are also called definitions. Antivirus receives the latest virus definitions by downloading the update released by the vendor.
In the Behavior-based malware detection technique, antivirus monitors the behavior of a program. If it finds the program’s behavior malicious, it blocks that program. The Behaviour-based malware detection technique can generate False Positive flags. For example, if an antivirus detects the behavior of a suspicious program, it blocks that program.
What is a False Negative in Cyber Security?
A False Negative flag is the inverse of a False Positive. The False Negative occurs when an antivirus software or Security Software fails to detect a malicious file or program. Some malware uses advanced techniques to hide themselves so antivirus software cannot detect and quarantine them. These uncaught malicious threats remain active on the user’s systems and possess a security threat.
How does a False Negative occur?
False Negative usually occurs when you have not updated your antivirus program. Antivirus programs need regular updates to detect newly released threats. If you run an antivirus with outdated virus definitions, your system will be prone to newer threats or malware attacks. This is because the new virus signatures are unknown to your antivirus. False Negatives are a serious security risk for your system.
How to tell if it is a Virus or a False Positive?
If your antivirus software has blocked a file or a program and you need that file or program, you can identify the authenticity of that file or program by using some methods. We have described these methods below.
- Using VirusTotal
- Searching for the file online
- Viewing the file signatures
Using VirusTotal
The first method by which you can identify the authenticity of a file or a program is to scan it on VirusTotal or another similar cloud service. VirusTotal is a cloud service that has several antivirus engines. When you scan a file on the VirusTotal website, these antivirus engines scan that file and then VirusTotal generates the report.
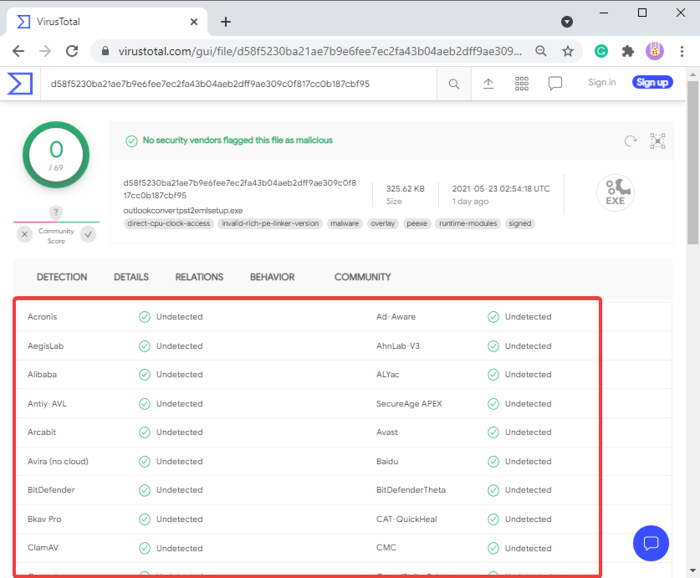
If your antivirus software has flagged a genuine program or file as malicious, you can scan it on VirusTotal and view the report. This report will let you know whether other antiviruses flag that file malicious or not.
Read: How to check if a File is malicious or not on Windows
Searching for the file online
The next method that you can use to identify whether a file or a program is malicious or not is by searching online. You can search online by using different keywords.
For example, if your antivirus program has flagged and quarantined a DLL file, say rundll32.exe, you can search for its authenticity online by using different keywords, like:
- What is rundll32.exe process
- Is rundll32.exe safe?
- Is rundll32.exe malicious?
While searching online, you will see the links to various websites and forums. To get authentic information, consider visiting trusted websites like TheWindowsClub. You can also read the reviews submitted by various users on different forums. This will also help you know the file’s authenticity or the program.
Viewing the file signatures
Another effective method that you can use to know whether a file or a program is malicious or a False Positive is by viewing its signatures. A genuine file is digitally signed by its vendor. You can view this information in file properties.
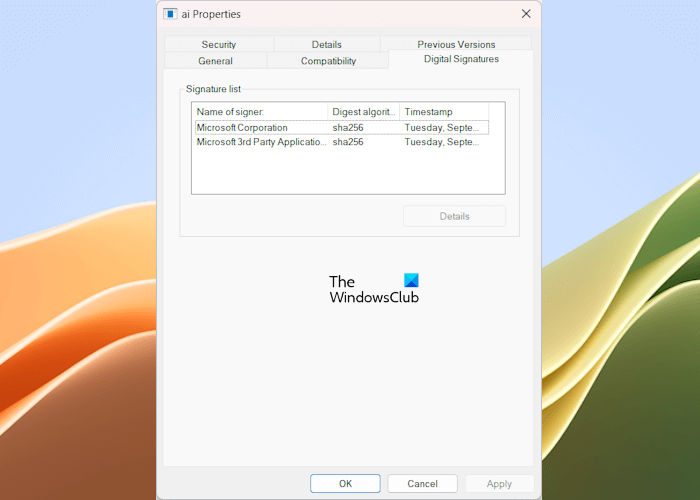
The following steps will help you with that:
- Right-click on the file.
- Select Properties.
- Select the Digital Signatures tab.
The Digital Signatures tab is available for executable files and services. Now, you can view the name of the signer under the Digital Signatures tab. The above image shows that the AI Host file Ai.exe is digitally signed by Microsoft. Hence, it is a genuine file.
If your antivirus has flagged a program as malicious and you want to view its Digital Signatures, you will not find the Digital Signatures tab by opening its properties from the Desktop shortcut. In this case, you have to open the properties of its executable file from the installation location. To do so, right-click on the desktop shortcut and select Open file location.
Read: Test if Antivirus is working or not.
How to remedy a False Positive action by Windows Defender?
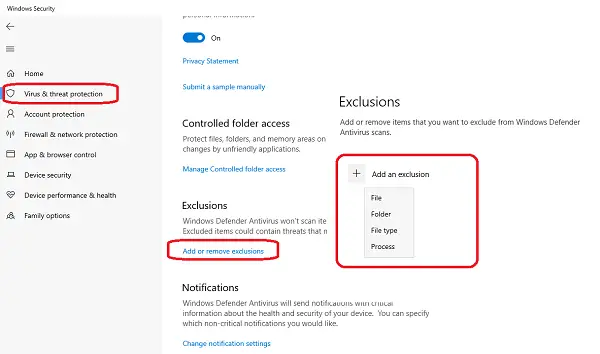
If Microsoft Defender generates a False Positive flag for a file or a program, you can tell Microsoft Defender about the authenticity of that file or program by adding it to the Microsoft Defender’s Exclusions list. After that, Microsoft Defender will stop alerting you about that program or stop blocking that program.
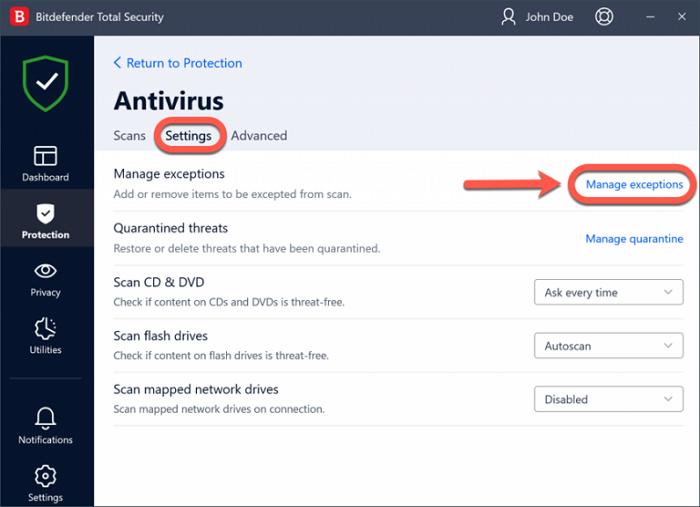
The option to add a file or a program to the exception or exclusion list is available in all antivirus programs. Hence, if you use a third-party antivirus, you can add that file to its exception list. Because of the difference in the user interface, the process to exclude a file or program is different in different third-party antivirus programs.
Read: How to tell if your computer has a virus?
Where do you report a false positive/negative to Microsoft?
Reporting the False Positives and False Negatives to Microsoft will help Microsoft correct the detections. This will lower the generation of False Positive flags and lower the chances of malware remaining undetected.
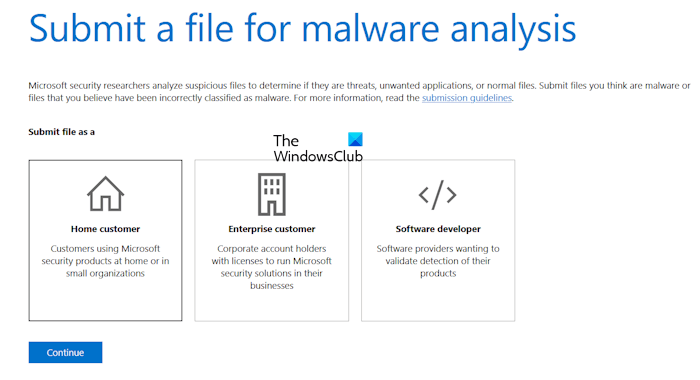
To report a False Positive or a False Negative (or malware) to Microsoft, you must visit the Sample Submission Portal and submit the file there. Now, select the most appropriate option from the following:
- Home customer
- Enterprise customer
- Software developer
After that, click Continue and sign in using your correct account credentials. Now, fill in the required details, attach the file, and click Continue.
I hope this helps.
What causes a False Negative result?
Usually, a False Negative result is caused due to the outdated virus definitions of antivirus software. Antivirus vendors release virus definitions via regular updates. You should download and install these updates regularly.
What is True Positive and False Positive in Cyber Security?
In Cyber Security, True Positive refers to the correct detection of a threat by an antivirus program or a Security Software. On the other hand, a False Negative is the incorrect detection of a threat, i.e., antivirus or security software has detected the genuine file as malicious.
Read next: EDR vs Antivirus: Which is best and why?
Leave a Reply