When we use a computer, some amount of heat is generated. Doing heavy tasks, such as playing heavy graphics games, generates more heat. The amount of heat generated is inversely proportional to a computer’s performance. This means that computers perform poorly at high temperatures. To lower the computer temperature, various components are installed. Heat Sinks are one of these components. In this article, we will see what is a Heat Sink and how it works.
What is a Heat Sink?
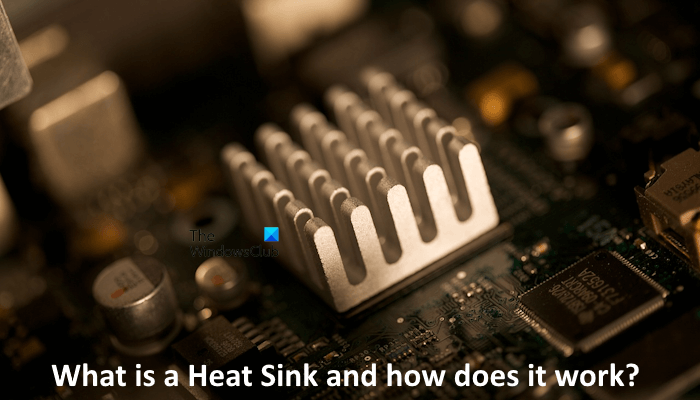
A Heat Sink is a piece of metal that is mounted on an electronic component to make the process of heat dissipation faster. It is a heat exchanger that transfers the heat generated by the electronic component into the fluid medium it contains.
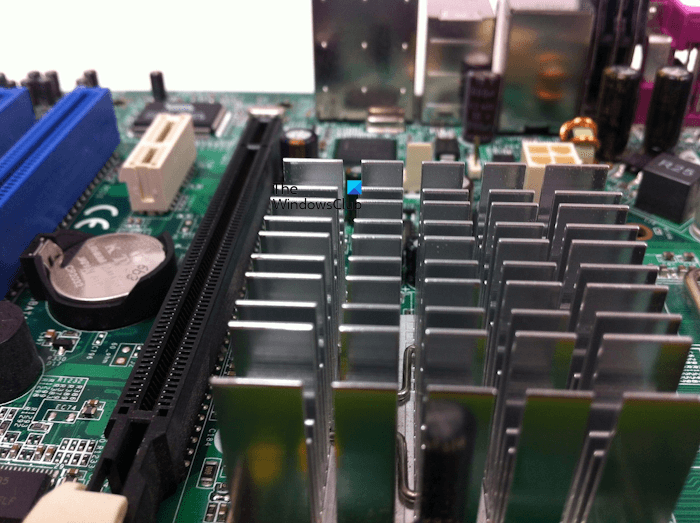
Heat Sinks can be of different designs but the functionality of all the Heat Sinks is the same. All Heat Sinks use a fluid as a medium to transfer heat into the environment.
How does a Heat Sink work?
A Heat Sink is an important component of a computer. Computers with Heat Sinks have faster and more effective cooling rates than computers without Heat Sinks. Let’s see how a Heat Sink works.
Heat sinks are installed on electronic components such as CPUs, GPUs, etc., and have raised fins. These fins increase the surface area of the Heat Sinks. If you have opened your computer case, you might have seen such a metallic structure with raised fins installed on your CPU.
The working process of a Heat Sink is simple. Conduction and convection are the principles on which they work.
- The Heat generated by an electronic component is transferred to the Heat Sink attached to it through conduction. Conduction is the process in which the heat is transferred from one object to another by direct contact. For the conduction process to occur, the two objects should touch each other.
- The heat transferred to the Heat Sink starts traveling from its base to its fins. Because a Heat Sink has a lot of fins, the transferred heat is distributed throughout all the fins.
- The heat is then transferred to the working fluid from the fins of the Heat Sink through convection. Convection is the process in which heat is transferred from one body to another through a fluid. In most Heat Sinks, the working fluid is air.
- With the airflow, the heat is transferred into the surrounding environment.
Type of Heat Sinks
Heat Sinks are commonly of the following two types:
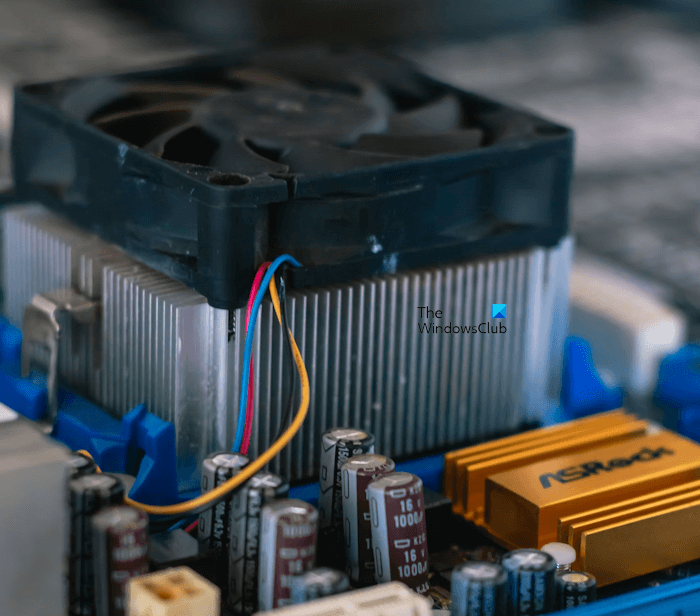
- Passive Heat Sink: A Passive Heat Sink is a piece of metal with raised fins. It transfers heat into the environment through the working fluid (air) through the natural airflow. Passive Heat Sinks are less effective than the Active Heat Sinks.
- Active Heat Sink: An Active Heat Sink uses an additional source to transfer heat into the environment. For example, if you install a fan on a Heat Sink, it will become an active Heat Sink. Active Heat Sink transfers heat into the environment faster with the help of the fan.
What is the best type of heatsink?
An active Heat Sink is the best type of Heat Sink. This is because it transfers heat into the environment faster than its counterpart, the Passive Heat Sink. Usually, it uses a fan to increase the heat dissipation rate.
Is a fan a heat sink?
No, a fan is not a Heat Sink. It is a source of blowing air and increasing the airflow. It can be installed on a Heat Sink to increase its heat dissipation rate. The Heat Sinks with fans have higher performance than those without fans.
Read next: How to lower CPU temperature in a computer.
Leave a Reply