If you are a network engineer or a normal user, you may need to find, open or block a virtual port, such as a TCP or a UDP port for an application. Virtual ports help you manage your network hardware and software with respect to the information traffic. In a layman’s language, virtual ports serve as the dedicated lanes for particular traffic such as website traffic, receiving emails, transfer of files and so on.
There are basically two types of virtual ports, namely TCP and UDP. TCP stands for Transmission Control Protocol; while UDP stands for User Datagram Protocol. TCP and UDP ports use different network protocols when handling information traffic. Network protocols are nothing but the set of rules and regulations of how certain information should be sent and received. However, the basis of a TCP or UDP port is IP, i.e. Internet Protocol.
Let’s see how these two ports defer in their features and functions.
How does a TPC port work?
A TCP port requires users to establish a connection between the sender’s machine and the receiver’s machine. It is quite similar to making a phone call. Once the connection is established between the sender and the receiver, the information can be transmitted back and forth, until the connection is broken externally.
Though TCP is the most complex transport layer protocol, it is also the most reliable protocol when it comes to receiving error-free information. The protocol makes sure that the destination machine acknowledges the receipt of the datagram. Only then it transmits the information. Hence, TCP is more commonly used than UDP.
How does a UDP port work?
A UDP port, on the other hand, doesn’t need users to establish a connection between the sender and the receiver to send the information. However, unlike a TCP port, the information sent over the UDP port may not reach the receiver. It is similar to sending a letter. It is not necessary that the user has received the letter. Hence, the information that needs to be broadcasted is sent over a UDP port. The user tuned over or listening to the specified UDP port can receive information.
UDP has low latency and offers a constant stream of information. Thus, a UDP is the perfect choice for streaming broadcasts, online video games, and a voice-over-IP (VoIP) streaming. As a result, a UDP port is used only when there is a specific need regarding information being sent.
Identifying the right ports
There are many virtual ports available for any PC; which range from 0 to 65535. However, each of these ports has a certain standard and is dedicated to a certain application. Out of these, some of the following ports use TCP and UDP.
- 20 (TCP): FTP (File Transfer Protocol)
- 22 (TCP): Secure Shell (SSH)
- 25 (TCP): Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)
- 53 (TCP and UDP): Domain Name System (DNS)
- 80 (TCP): Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
- 110 (TCP): Post Office Protocol (POP3)
- 143 (TCP): Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP)
- 443 (TCP): HTTP Secure (HTTPS).
It is possible to check which of the ports on your Windows PC are open or close. If you wish to block or open a certain TCP or UDP port, then here is the process.
Finding an open TCP or UDP port
Open the Start Menu. (For Windows 10, press the Windows button) and type CMD. Now click on Run as Administrator option.
When the Command Prompt window opens, type Netstat -ab and press Enter. A list of TCP and UDP ports starts appearing along with the IP address and other details.
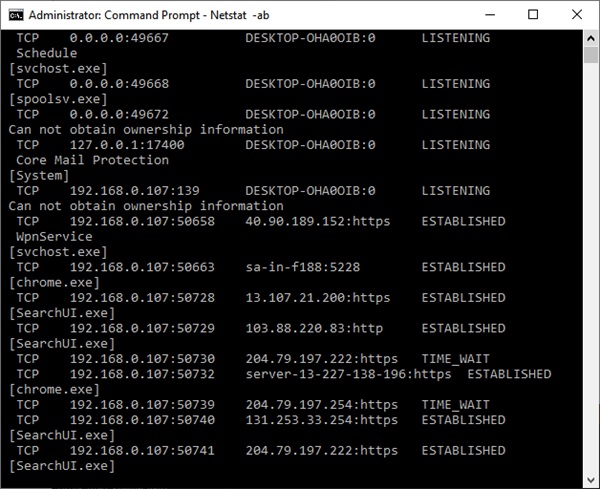
The longer you wait, the bigger the list of open ports becomes. Wait until the complete list has appeared in the window. Once the list fully appeared, Press CTRL+C and CTRL+V to copy and paste the information into Notepad or any other text editor.
As you can see in the above image, the information in the brackets refers to the name of the program that is using an open TCP or UDP port. Next to the protocol name, you can see the IP address and the port number after the colon. For example, in 192.168.0.107: 50741, the numbers 192.168.0.107 are the IP address, while the number 50741 is the port number.
Read: How to check what Ports are open?
Finding a blocked TCP or UDP port
To know which of the ports are blocked by Windows Firewall, follow the next steps.
The first step is the same as finding an open TCP or UDP port. Open Start Menu by pressing the Windows button and type CMD. Now click on Run as Administrator option.
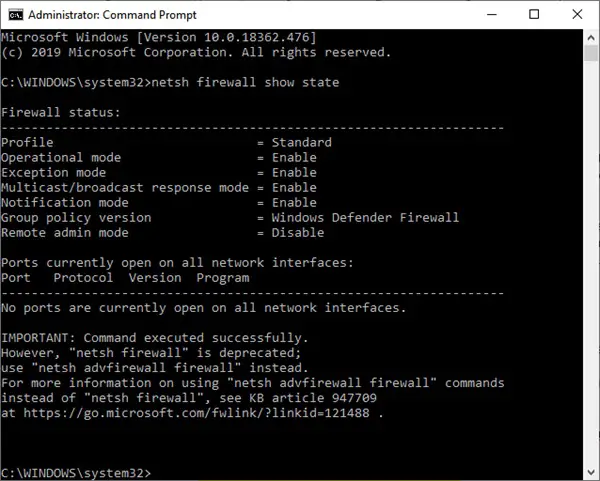
When the Command Prompt window opens, type following command: netsh firewall show state
Some ports may be blocked by the router or ISP and those may not be listed in the above list. To find those ports, type the following command: netstat -ano | findstr -i SYN_SENT
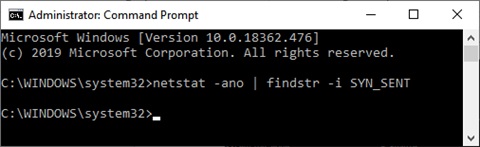
If this command doesn’t return any list, it means none of the ports are blocked by the router or ISP.
How to open or block a TCP or UDP port
Now since you have identified the TCP and UDP ports on your Windows PC, here comes the most important part.
First of all, you may need to open a port for an application to run smoothly. On the other hand, you may need to block certain ports as they are no longer being used and may pose as a gateway for threats. Hence, such ports are blocked by the firewall.
Follow the next steps to open or block a TCP or UDP port.
Open the Start Menu by pressing the Windows-key. Type Windows Defender Firewall, and select Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security from the results.
The following window opens.
Click on the Inbound Rules tab on the left side menu.
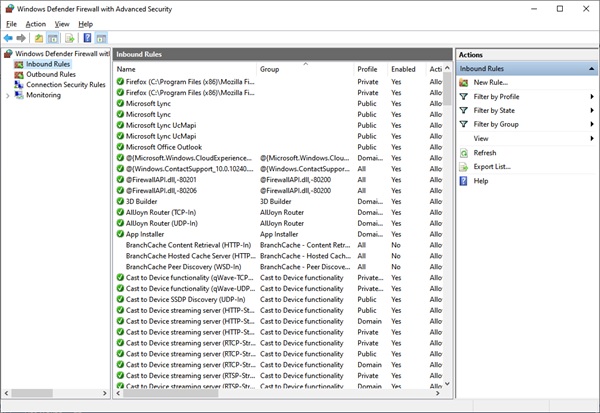
Click on the New Rule… tab from the Actions pane on the right side menu. When this window opens, select the Port radio button and click Next.
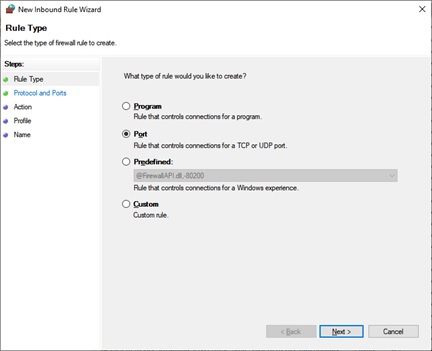
When pressed Next tab, the following window of New Inbound Rule Wizard opens. In this window, you can select the type of port you want to open or block. You can also select whether you want to open or block all the ports of the selected type or a specific local port. Specify the number or a range of the local ports that you wish to open or block. And click Next.
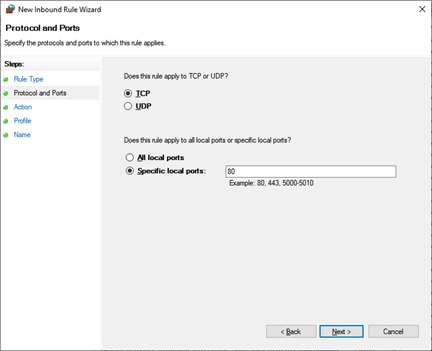
The following window opens when you click Next. Here you can open the ports by selecting Allow the connection or Allow the connection if it is secure radio buttons. Select the third radio button Block the connection to block the specified ports.
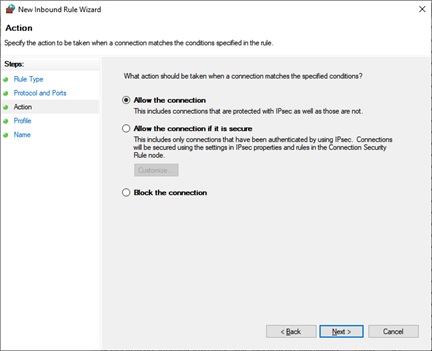
Now select whether the rule applies to Domain, Private or Public or all of these. Click Next.
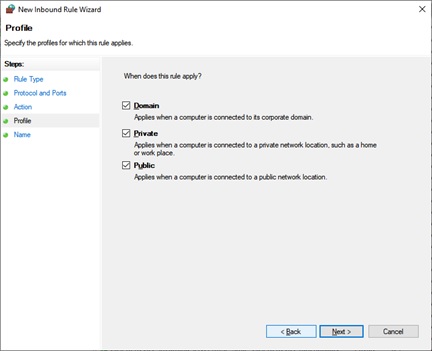
The following window opens when you click Next. In this window, specify a Name for this new Inbound Rule. You can also specify which ports have been blocked or opened in the Description section.
Click Finish to create this new Inbound Rule.
Please note that sometimes after blocking a certain port, apps may not work properly. You may also face issues while connecting to certain resources. This means the port you blocked may be required to be open. You can undo the blocking of ports at any time following the same process.
Read next: How to monitor TCP, UDP Communication in Windows with PortExpert.
Leave a Reply