If you have ever heard about EFI or seen an EFI System Partition (ESP) in Windows and wonder what it is, then this post will help you understand. We will talk about EFI, how you can identify the EFI partitions, what it contains, and whether you can delete it.
What is EFI Partition in Windows?
EFI stands for Extensible Firmware Interface system partition which is generally a partition in data storage devices like hard disk drives or SSDs used by a computer system that has the UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface).
When you boot your computer, the UEFI firmware loads the file stored on EFI or ESP (EFI System Partition) to start the currently installed operating system on your system and various system utilities. The ESP contains the boot loaders and kernel images, device driver files, and other utilities required to run before booting the OS.
The EFI is a minimal partition of around 100 MB, which is formatted with FAT32. This is where all the applications needed for the startup of windows are stored. You can access the EFI system partition on Windows by running the mountvol / s command.
How to identify EFI System Partition Windows 11/10?
The EFI partition is crucial; that is why it is hidden so that a general user won’t find it accidentally in File Explorer. Here are various tools using which you can identify the EFI partition.
- Windows Disk Management Tool
- Diskpart Tool
- Third-Part Disk Tools
It is important that you do not delete the EFI partition using these tools. However, accidents can happen and ensure you have created a System Image before any of these operations.
1] Using Disk Management Tool In Windows
The Disk Management tool is a Windows management tool used to rename, resize, partition, and formatting disks. It lets you handle the management of hard disk partitions without rebooting the system and any interruption. You can create, delete and format partitions, change drive letters and paths, convert empty MBR to GPT disk, initialize a brand new disk before even using it, etc.
Here are some of the most convenient ways to open Disk Management and identify EFI partitions.

- Use the Windows hotkey Windows+R to open the Run window.
- Type Diskmgmt.msc and press the Enter key.
- The Disk management will open, and you can identify EFI partitions from there. Look for a partition with EFI written on it.
2] Using Diskpart Tool
DiskPart is a command-line disk partitioning utility. The diskpart interpreter allows you to manage your computer drives, including virtual hard disks, partitions, volumes. It lets you create, delete and modify partitions on your hard drives or USB your computer can detect. DiskPart is a perfect alternative to Disk management tools as it is more powerful and suitable for technical users.
You have to always open diskpart with administrator permission. To open diskpart here is a simple way of doing so.
- Type Diskpart in the search box and find it from there.
- Once you see Diskpart in the search result, click to launch.
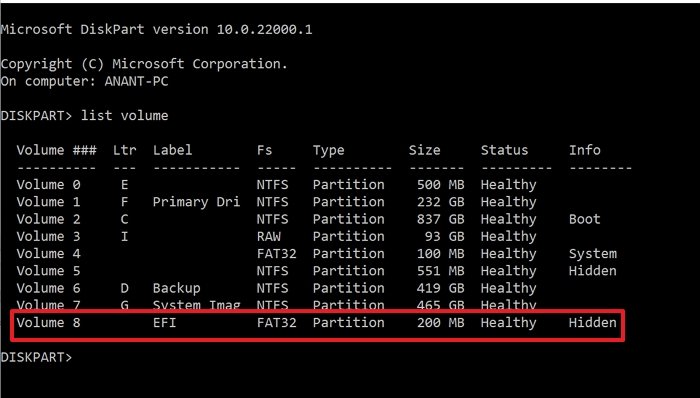
- Type
list volumeand press the Enter key - It will display all the volumes or partitions available on the PC.
- Look for a partition that has Labeled as EFI and Fs as FAT32. It is also marked as hidden.
Read: Windows detected that the EFI system partition was formatted as NTFS
3] Using Third-party Tools
Apart from the traditional tools, Windows provide us with managing partitions and EFIs. There are several third-party software that provides these services for a better experience.
Paragon Partition Manager
Paragon Partition Manager is free-to-use software that lets you organize your hard drives and helps you gain extra space in existing partitions. It offers many features, like resizing/moving partitions and undeleting partitions. You can recover data if you delete a partition by mistake. You can create, delete, and expand partitions. It also allows you to change the label of a partition, and you can check for errors on selected partitions to fix them.
To locate the EFI partition, follow the steps as below:
- Download and install the software, and then launch it.
- Once it identifies and loads all the drives, locate the primary drive on which Windows is installed
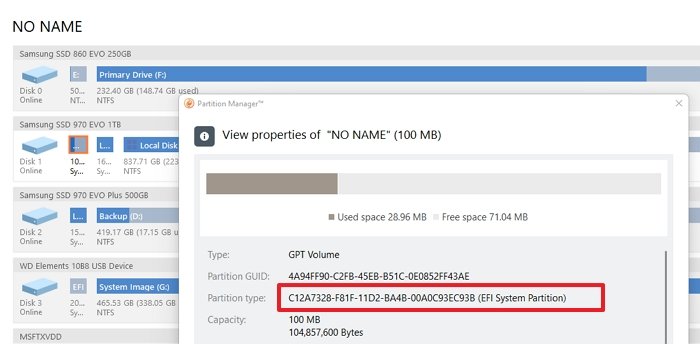
- It will be available in three parts—Two System Reserves and One Local Disk
- Of these two, one will be 100 MB. Select it, and then click on Properties
- In the details window, notice EFI System Partition as part of the description.
GParted
GParted is a free-to-use software for partition manipulation to manage your disk partitions graphically. With GParted, you can copy, move, resize the partitions without any data loss. It also lets you attempt data rescue or recovery from lost or deleted partitions. You can also create space for the new OS, change labels, set new UUID, etc.
Once you open the GParted tool, it will help you identify the EFI partition. If you cannot see any label, look for the 100 MB partition, which is hidden.
Should I delete the EFI Partition?
You should never delete the EFI Partition unless you have a solid reason behind it and know what you are doing. It is where your OS stores all the boot files. If you delete this, it is basically like deleting your OS. You can only attempt to delete it when you are wiping down an entire drive and have a full-fledged operating system on the other drive or a clone or backup.
Read: Can I delete Recovery Partition in Windows?
How can I see what’s in the EFI Partition?
As EFI is hidden from the File Explorer, you can use the mountvol /s command to mount the EFI system partition on the specified drive. Make sure to choose a drive letter that is not occupied by any other drive.
How can I delete the EFI Partition in Windows?
We will use DiskPart to delete EFI partitions, as Diskpart is a command-line utility that manages drive partitions. Here are some simple steps that you can follow to delete the EFI partitions:
- Open the command prompt and run it as Administrator.
- Enter diskpart to begin the utility.
- Use the list disk command to show all the disks. Find the disk with EFI partitions.
- Enter select disk #. Here # represents the disk number.
- Show the selected partition using the list partition command
- Identify the EFI partition, and it will be of Type: System.
- Enter select partition #
- Finally, enter the command delete partition override.
How Do I Restore The EFI Partitions?
Mistakes can happen unintentionally; thus, accidentally deleting your EFI partition may be one of them. Here, we will discuss a step-by-step process of restoring an EFI partition by command prompt.
- Boot the computer using Windows installation media or Windows recovery disk.
- Run the following commands to shrink a partition for an unallocated space
diskpart- `list disk`
select disk #(choose the disk where you want to add the EFI partition)- `list partition`
select partition #(choose the partition which you want to shrink)- `shrink desired=100` (shrink the chosen partition by 100 MB)
- Run the following commands to create the EFI partition
create partition efi size=100format quick fs=fat32assign letter=h(you can choose whatever letter which is not already in use)exit
- Use the given commands to copy the boot files from Windows partition to EFI partition and create a BCD store in it
bcdboot C:\windows /h H:(c is the drive letter whereas H is the letter assigned to the EFI partition)exit
- Reboot your computer
What Is The Difference Between EFI And MBR?
MBR (Master Boot Record) is a slightly older style of recognizing bootable disks and media that supports 2TB of HDD. BIOS uses the MBR to save information about all the data in Hard drives, while UEFI uses the GUID partition table (GPT). MBR only uses 32 bits in its tables, which results in only 4 physical partitions. However, UEFI is platform-independent; hence, it provides better booting time and full speed of the computer.
Does Upgrading To EFI Offer Any Benefits?
EFI files are stored in a particular partition system called ESP on the hard disk. UEFI has discrete driver support, UEFI provides faster booting time, supports hard drive partition greater than 2TBs, supports more than four partitions on a single drive, efficient system, and power management. So yes, there are many benefits of upgrading to EFI.
Does Windows 11 Need An EFI-based Partition To Upgrade?
Yes, Windows 11 needs a UEFI-based partition because it is not compatible with BIOS or Legacy compatibility mode; therefore, it must run with UEFI. The users must enable secure boot, as the secure boot option is associated with UEFI-based computers.
In this post, we’ve discussed the majority of points that are associated with EFI partitions. Above are all the basic tasks you can perform with EFI partitions and some comparisons with their counterparts. But ensure you have a proper backup of your data if something goes wrong, and always know what you are doing.
Leave a Reply