NavIC stands for Navigation with Indian Constellation. It is also called IRNSS (Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System). NavIC is an alternative to the American Global Positioning System (GPS) but is currently limited to the Indian region. That’s why it is also called IRNSS. In this article, we will also compare NavIC with GPS and see whether it is better than GPS or not.
What is Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (NavIC)?
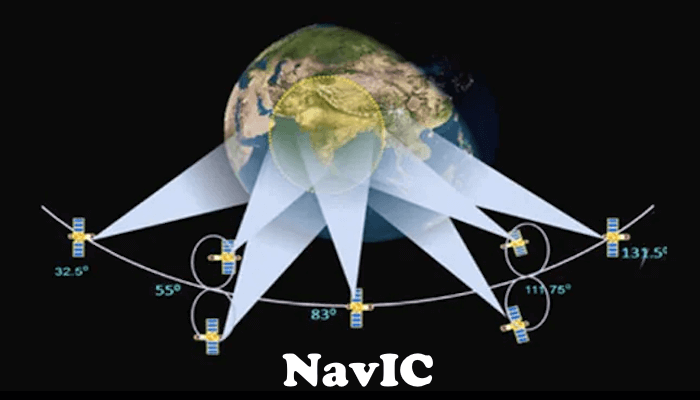
NavIC is developed by ISRO (Indian Space Research Organization). It is a constellation of 7 satellites. Out of these 7 satellites, 3 are the Geostationary satellites, and 4 are the Geosynchronous satellites.
NavIC is developed to provide accurate position information to the users in India. Currently, NavIC covers the entire area of India and 1500 km beyond the boundaries of India. ISRO is planning to expand the area coverage of NavIC in the future.
The Journey of NavIC: A Quick Recap
This was when the Kargil War took place in 1999. At that time, the only navigation satellite system available was GPS (Global Positioning System), developed by the USA. India was also dependent on GPS at that time. The situation was critical.
To handle this critical situation, the government of India asked for satellite images of the Kargil region from a leading western country so that India could identify the correct locations where the attackers were hiding themselves. The country denied sharing the satellite images with India.
From that time, India decided to develop its own navigation satellite system.
The Government of India approved the NavIC project in 2006. The project was expected to be completed in late 2011 but became operational in 2018. When the project was approved, it was called IRNSS. Later, in 2016, the Prime Minister of India gave it another name, NavIC. The first three letters of the name NavIC mean Navigation, and the last two letters I and C mean Indian Constellation. The name NavIC is uniquely taken from the Indian language, which means sailor or navigator, hence defining the project’s beauty.
Geostationary Satellites vs Geosynchronous Satellites
Before we discuss NavIC in more detail, let’s discuss these two terms. NavIC uses the following two types of satellites:
- Geostationary satellites
- Geosynchronous satellites

When a satellite revolves in an orbit that is circular and directly above the Earth’s equator, that satellite is called a Geostationary satellite, and the orbit is called a Geostationary orbit. These satellites are called Geostationary because they seem to be stationary for a person on the Earth’s surface.
When a satellite is inclined to a certain angle to the Earth’s equator, that satellite is called a Geosynchronous satellite and the orbit in which it revolves is called a Geosynchronous orbit. The Geosynchronous orbit is slightly elliptical.
The satellites in the Geostationary orbit revolve around the Earth in the orbit exactly above the Equator from West to East. Therefore, the angle between them and the equator is 0 degrees. These satellites take 23 hours 56 minutes and 4 seconds to complete one revolution. This angle is not 0 degrees in the case of Geosynchronous satellites. To match the speed of the Geostationary satellite with the speed of Earth’s rotation, they should revolve about 3 Km per second at an altitude of 35786 Km.
Number of satellites in NavIC
The total number of satellites used in NavIC is 7. These are:
- IRNSS-1A: It is the first satellite launched for the IRNSS space program. It is a Geosynchronous satellite that was launched on 1st July 2013.
- IRNSS-1B: It is the second satellite for the IRNSS space program. It is a Geosynchronous satellite and its launch date was 4th April 2014.
- IRNSS-1C: The third satellite of the seven satellites constituting the IRNSS program is IRNSS-1C. It is a Geostationary satellite and was launched on 16th October 2014.
- IRNSS-1D: IRNSS-1D is the fourth satellite constituting the IRNSS space program. It is a Geosynchronous satellite and was launched in March 2015.
- IRNSS-1E: The fifth satellite of the IRNSS space program is IRNSS-1E. It is a Geosynchronous satellite that was launched on 20th January 2016.
- IRNSS-1F: It is the sixth navigation satellite that was launched in March 2016. It is a Geostationary satellite.
- IRNSS-1G: IRNSS-1G is the seventh satellite. It is a Geostationary satellite and was launched on 28 April 2016.
Applications of IRNSS or NavIC
Some applications of the IRNSS space program or NavIC are:
- Terrestrial, aerial, and marine navigation,
- Vehicle tracking and fleet management,
- Disaster management,
- Terrestrial navigation aid for hikers and travelers,
- Visual and voice navigation for drivers, etc.
NavIC vs GPS: A comparison
Above, we have explained about NavIC. Now, let’s see the difference between NavIC and GPS. We will also see if it is better than GPS or not.

GPS or Global Positioning System is a navigation system developed by the US Department of Defense. Because it is a Global Navigation System, it is being used by users across the globe. Today, most of the world’s navigation is based on GPS. Even Google Maps and other food delivery apps also use GPS for navigation.
- NavIC is the indigenous navigation system of India developed by ISRO. It is similar to GPS, but it covers only the area of India.
- GPS is a popular navigation system, whereas NavIC is not as popular as GPS. NavIC has a local reach, whereas GPS has a global reach.
- GPS uses 31 satellites, whereas NavIC uses 7 satellites. GPS can provide an accuracy of up to 20 meters, whereas NavIC provides an accuracy of up to 5 meters. NavIC has a greater accuracy as compared to GPS. Therefore, it is the best navigation system for defense and research applications.
- Currently, NavIC provides better accuracy than GPS. If we compare both of these navigation systems in terms of area, GPS covers the entire globe, whereas NavIC is only limited to India for now.
The goal of the government of India is to make NavIC a global navigation system like GPS in the future.
India launched the first Indigenous NavIC-based chip
Elena Geo Systems, a Bengaluru-based space technology company, launched the NavIC-based chip earlier this year (2023). This chip will provide high precision and accuracy for all types of NavIC-based applications. This chip is named the NavIC processor because it has many cores that are capable of servicing the requirements of NavIC.

In a statement, Lt. Col. Velan said:
We are thrilled to present India’s first fully designed and developed NavIC chip. The processor will give India a huge edge as both the government and private sector can move away from their dependence on the American Global Positioning System (GPS). Elena is in the process of patenting the technology and the product which has been developed by our dedicated R&D team.
Is NavIC available for public use?
NavIC will be available for public use after the success of NavIC. The Government of India planned to make it available to all users in India. The minister of state for Electronics and Information Technology said in a statement that all smartphones must support NavIC by the end of 2025.
Recently, in September 2023, Apple announced that the newly launched iPhone 15 Pro and iPhone 15 Pro Max will have NavIC support.
To complete the target to introduce NavIC in all smartphones by the end of 2025, the government of India will also offer incentives to the companies that will use NavIC-supported chips in their smartphones.
We aim to establish an incentive structure that will encourage companies participating in the PLI schemes to adopt NavIC-supporting chips designed or manufactured in India.
How can I access NavIC?
The introduction of NavIC into smartphones and making it available for Indian users is a challenging task as it requires a great investment. According to the smartphone manufacturing firms, it will also raise the production cost of smartphones. However, the Government of India has planned to complete this target by the end of 2025.
If you want to access NavIC, you should have a smartphone that has NavIC-supported hardware. However, there is one more way to access and use NavIC on your smartphone. This is by installing the Mappls app.
The Mappls app is developed by MapMyIndia. It is a NavIC-based Indian navigation platform that uses IRNSS or NavIC data. You can install it on your smartphone. However, NavIC will become fully operational for all users after the installation of compatible hardware.
You can also access NavIC via the Bhuvan portal of India. It is a GIS portal that provides maps and terrain data with the help of IRNSS or NavIC data. To access Bhuvan, you have to visit the official website, bhuvan.nrsc.gov.in.
Does NavIC have an app?
NavIC is not an app. It is a navigation system developed by ISRO. It does not have any apps. The Government of India has planned to integrate NavIC into all smartphones by the end of 2025. Hence, the navigation apps on these smartphones will use NavIC.
How do I use NavIC on Google Maps?
To use NavIC on smartphones, they should have compatible hardware, including the NavIC chip. This is the reason why current smartphones do not have NavIC. Google Maps uses GPS for navigation. Upcoming smartphones will support NavIC. Therefore, Google Maps in the NavIC-supported smartphones can use NavIC for navigation purposes.
When will NavIC start working?
NavIC is currently operational. The Government of India uses its data for research and defense purposes. The Bhuvan platform also uses NavIC data and APIs from MapMyIndia. Bhuvan is a GIS portal developed by NRSC (National Remote Sensing Center), which is one of the primary centers of ISRO.
Currently, normal users cannot use NavIC on their smartphones because of the incompatible hardware. We have already explained above that the Government of India has set a target to introduce NavIC to all smartphones by the end of 2025. Since then NavIC will become operational for normal users.
Is NavIC better than Google Maps?
NavIC is not an app. It is an indigenous navigation system of India developed by ISRO. Currently, NavIC is not available to users because it requires compatible hardware to be installed on smartphones. On the other hand, Google Maps is an app that comes pre-installed on all Android smartphones. Therefore, you cannot compare NavIC with Google Maps because the former is the navigation system and the latter is an app.
Will NavIC replace GPS?
GPS uses 31 satellites, whereas NavIC uses only 7 satellites. That’s why GPS is a global navigation system, and NavIC is a regional navigation system of India. According to the Government of India, NavIC will be installed on all smartphones by the end of 2025. Hence, there is a possibility that NavIC will replace GPS in India. But if India wants to replace GPS globally, it has to make NavIC a global navigation system.
Read next: What is UPI ID and how does it work?
Leave a Reply