We have recently spoken about IP routing, but there is something else that needs our attention, and it is all about the types of routes found in a routers routing table. It might sound confusing but worry not; everything will make a lot of sense in just a moment.
What is Routing?
To put it simply, routing is a process that is performed by network layer devices. It will deliver packets by selecting an optimal path from one network to the other.
What are the types of Routing?
At the moment, the three types of routing are as follows:
- Default routing
- Static routing
- Dynamic routing
Types of Routes explained
The following information will talk about the different types of routes and some of their advantages and disadvantages:
- What is Default routing?
- What is Static routing?
- What is Dynamic routing?
1] What is Default routing?
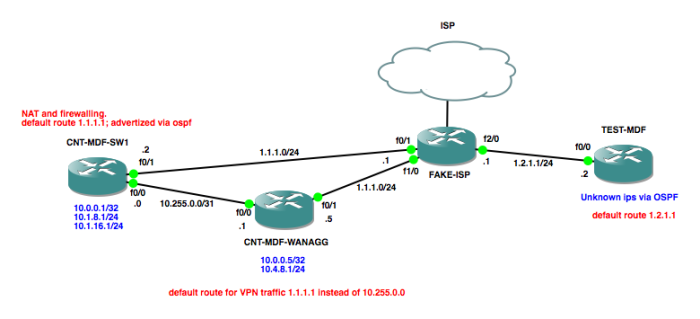
When it comes down to Default routing, this is basically a situation where the router is constructed to send all packets on the way to a single router. It matters not to which network the packet belongs to because it will be forwarded to the router that was configured for Default routing.
2] What is Static routing?
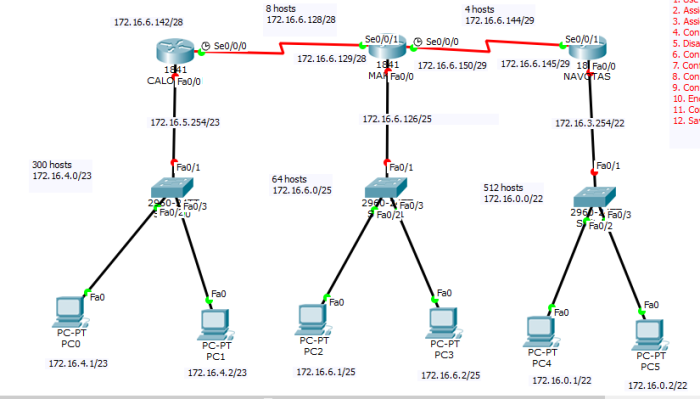
OK, so what is Static routing all about? Well, it is a process that requires us to add routes to a routing table manually.
- Advantages
This is great because an inexpensive router can be used to get the job done due to the fact that there are no routing overheads for the CPU to deal with. Furthermore, it has increased security because only the administrator can allow routing to other networks.
Additionally, we should point out that there is no bandwidth usage between any of the connected routers.
- Disadvantages
Static routing will not be the best if you run a large network because administrators will need to manually add every route to each network. If you can manage to do this without minimal problems, then go ahead.
Another problem, the administrator needs to have a good enough knowledge of the topology of the route.
Read: What is IP routing?
3] What is Dynamic routing?
In terms of Dynamic routing, some might view it as better than the rest due to its automatic nature. You see, it will make adjustments to routes itself that are in line with the current state of the route in the routing table.
From our understanding, Dynamic routing uses specific protocols to locate network destinations. These protocols are RIP and OSPF.
- Advantages
OK, so Dynamic routing is easy to configure when compared to the others. Not only that, but it is more effective in choosing the best route to a destination remote network.
- Disadvantages
Because much of the work is automatic, Dynamic routing uses more bandwidth and CPU power. Additionally, it is less secure than Static routing.
Leave a Reply