When almost everything is shifting online in the internet generation, it is necessary to stay connected when remote. Tablets and mobile phones help a lot, but laptops could not and cannot be replaced soon. Laptops or Mobile PCs are a necessary work requirement, making it essential to find a way to keep them connected to the web whenever they are mobile. However, unlike phones and tablets, very few mobile PCs have inbuilt Wi-Fi adapters. Thus, most users depend on external Wi-Fi adapters for their needs.

Network Connectivity issues with Hotspots and Wi-Fi adapters in Windows 11/10
However, many users face connectivity issues with Hotspots and Wi-Fi adapters – e.g., Slow Internet despite all parameters being up to the mark, the poor performance of the W-iFi network, and continual disconnection/dropping of the Wi-Fi network.
Cause behind connectivity issues while running a laptop that is connected to a wireless access point
One prominent cause of the issue where a laptop shows connectivity problems while attempting to connect to hotspots is that the Wi-Fi adapters might not follow the 802.11 protocol.
To understand the cause better, the power saving feature because of the 802.11 protocol is already included in the laptop’s operating system. To save power, the power plan of the mobile PC would be set to Balanced by default.
However, by default, when the laptop is connected to a power source, the wireless adapter uses the Maximum performance mode instead of the Balanced mode. It means that the 802.11 power save mode is switched OFF.
If the wireless adapter using the 802.11 protocol is set to save power and is willing to enter the sleep mode, the adapter signals it to the wireless AP. To send the signals, the adapter sends them in the form of 802.11 frames. While doing so, the following should happen:
- When the wireless access point receives the 802.11 frames, that signal that the adapter is set to the power saver mode, the wireless AP should recognize this and enter the power saving mode itself.
- The access point buffers the packets to the client network adapter.
- The client network adapter receives the packets when its radio turns ON.
If the wireless access point does not follow the 802.11 protocol, it will keep sending the packets to the client network adapter even though its radio is turned OFF. In this case, these packets would get lost.
Solutions for connectivity issues while running a laptop that is connected to a wireless access point
While there is no known fix to this issue other than changing the hardware of the wireless access point, which might be impractical in most cases, here are two workarounds that might help:
1] Connect the laptop to a power source
Keep the laptop connected to the power source when using the wireless access point. It sets the laptop to the Maximum performance mode and switches OFF the 802.11 power save mode.
2] Change the power settings of the power plan
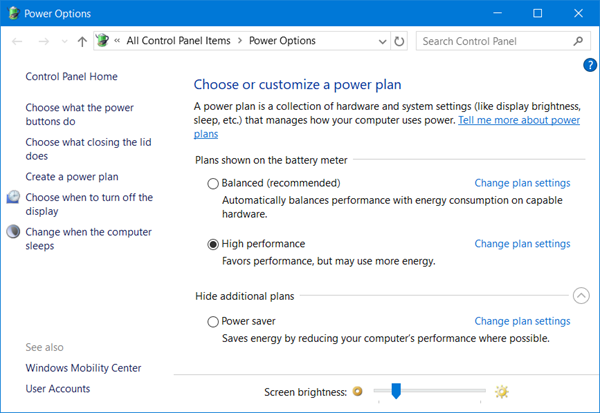
The current power plan of the laptop could be changed from Balanced to High Performance, or the settings on the Balanced power plan could be changed such that the battery is set on High Performance. This post will show you how to configure Power Plans.
Does it help?
If not, there are more posts related to connectivity issues:
- Network & Internet connection problems
- No Wi-Fi after upgrading to Windows 10
- Windows 10 cannot connect to the Internet
- No Internet Access in Windows 10
- No internet, secured error in Windows 10
- Dial-up Error 633 The modem is already in use or is not configured
- Limited Network Connectivity message.
Why does my PC randomly lose connection?
It is primarily because of an issue with the hardware or a driver issue. The best approach to fix it is resetting the adaptor, updating the driver, and setting up the connection again. You may also want to check if the signal from the router is not weak.
What happens if you reset Network Adaptor?
When a network adaptor (Wi-Fi or Ethernet) is reset, it will forget every connection made to a router or hotspot, including IP address and any other customization. You will have to reconnect to all previous connections.