In Windows, WiFi should connect automatically as soon as your computer starts. However, we have noticed that the automatic connection is falling. In this post, we will discuss what to do when a Windows 11/10 computer does not connect to WiFi on startup.
Why does Windows 11 not connect to Wi-Fi automatically?
Windows 11 will not connect automatically to the WiFi if you have not enabled the option in the network’s profile. If you encounter the issue even after enabling the option, tweak the power management options to resolve the issue. But if that is to no avail, you need to delete the Wlansvc files.
Windows 11 does not connect to WiFi on startup
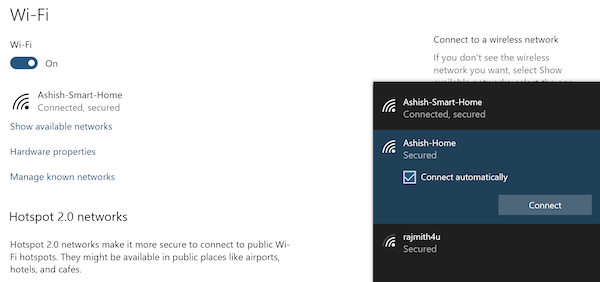
There can be multiple reasons for this behavior. So unless you have changed the WiFi connection credentials recently, here is how you can make Windows 11/10 connect to WiFi automatically:
- Opt-in for Auto connection
- Disable the Power Saver option on Wi-Fi adapter
- Adjust Wi-Fi adapter power management settings
- Delete Wlansvc Files.
Make sure that the WiFi strength is enough for the laptop to detect and connect. If you have a weak signal, then you may need to get closer to the router.
1] Opt-in for Auto connection
When you connect to a WiFi connection, there is a checkbox available. When you select it, it will make sure to automatically connect to the WiFi connection the next time it finds it. You may have forgotten to check the option.
Windows 11:
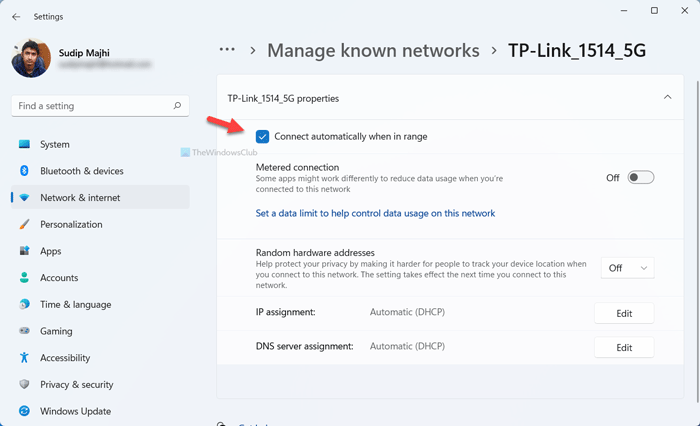
- Open Settings.
- Navigate to Network & internet > Wi-Fi.
- Now, click on the connected network.
- Now, make sure to have Connect automatically when in range is enabled.
Windows 10:
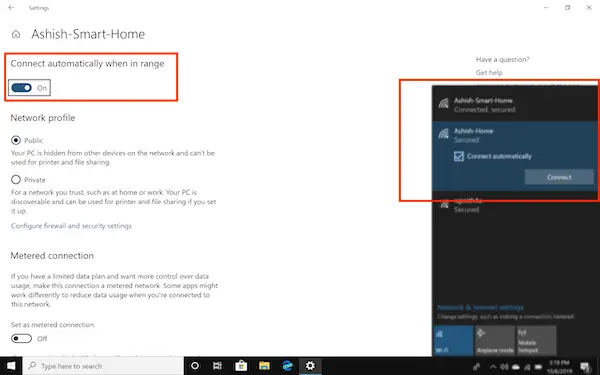
- Click on the Wifi Connection or Internet connection icon in the system tray.
- It will open the list of networks. Connect to the one you want, and then select it.
- Click on the Properties link to open Network Properties
- In the network profile screen, toggle the option that says the Connect automatically when in range.
The next time you start your computer, it will automatically connect.
2] Disable Power Saver option on Wi-Fi adapter
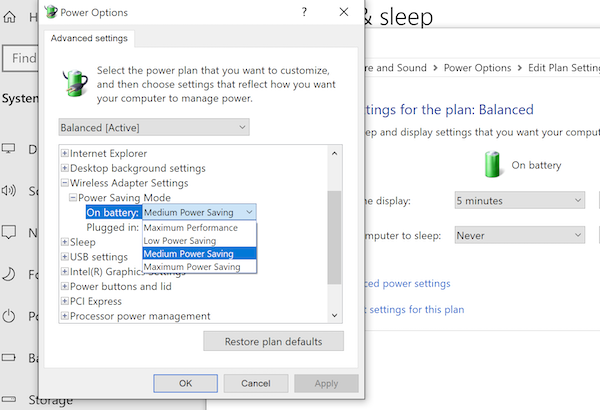
When using a laptop, the Battery Power Saver option on the WiFi Adapter can turn off WiFi when not in use or sleep mode. Here is how to change it
- Double-click on the Battery Icon in the System tray. Then click on the Battery Settings link.
- It will open the Battery section. Next, click on Power and sleep settings
- In the Power and sleep settings, locate the Additional power settings link in the right part. Click to open Power Options.
- Then for any selected plan, click on Change plan settings > Change advanced Power settings. Click to open.
- In the Power Options Advanced settings window, find Wireless Adapter settings
- Expand, and you will have options; On Battery and Plugged in.
- The default is Medium Power Saving. You can change it to Maximum Performance or Low Power Saving. The same, you can apply it for Plugged in the state.
Done that, the Wifi should automatically connect to the existing network.
3] Adjust Wi-Fi adapter power management settings
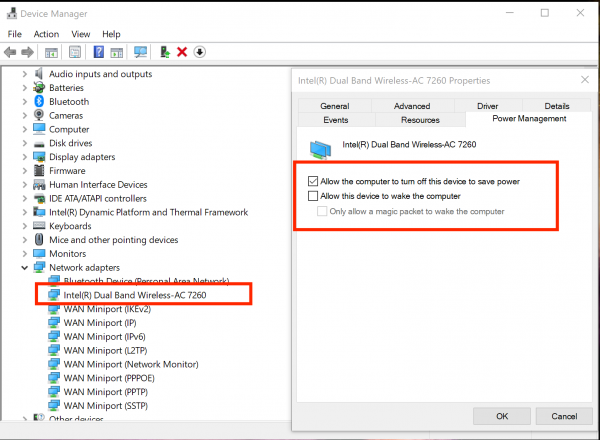
- Use WIN + X + M to open the Device Manager
- Expand the Network adapters list, right-click on your installed network adapter, and select Properties.
- Under Power Management, uncheck the box that says Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power.
If the reason is power management, then it will make sure that the OS doesn’t stop any Wifi connection. However, it usually happens when in low battery.
4] Delete Wlansvc Files
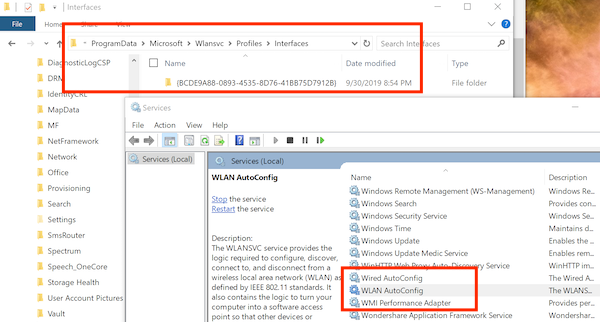
WLANSVC or WLAN Auto Config Service helps computers discover a wireless network, and connect to it. If the files where it stores existing networks are corrupt, then it can be a problem. Here is how you can refresh it:
- Type services.msc in the Run prompt and hit Enter.
- In the Services snap-in, locate WLAN AutoConfig.
- Right-click, and click on stop to stop the service.
- Using File Explorer navigate to
C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Wlansvc\Profiles\Interfaces
- Delete all the folders inside it.
- Restart the WLAN AutoConfig service, and then reconnect to networks again.
There are a few additional tips I would suggest. You can try to update or reinstall network drivers, run Windows Network Troubleshooter, or remove and add an adapter again through the device manager.
We hope these tips were useful and you can understand them clearly.
Leave a Reply