How does Windows 11/10 manage to run using smaller space on local storage in tablets, laptops, etc? Windows uses two distinct factors to ensure that the operating system takes up as little space as possible. It has to fit on a variety of devices with different storage limits, and under those terms, it will not be feasible if the operating system takes up much space. Lower storage space also means faster operating system work.
How Windows 11/10 saves space on devices
The first of the two factors is file system compression. The second one is a recovery enhancement system that we’ll talk about in the next section.
Windows 11/10 System Compression
Windows achieved significant footprint reduction using Windows Image Boot or WIMBOOT. This feature enabled Windows devices to have all the goodness of an efficient compression algorithm without compromising responsiveness. Windows compaction is the evolution of WIMBOOT!
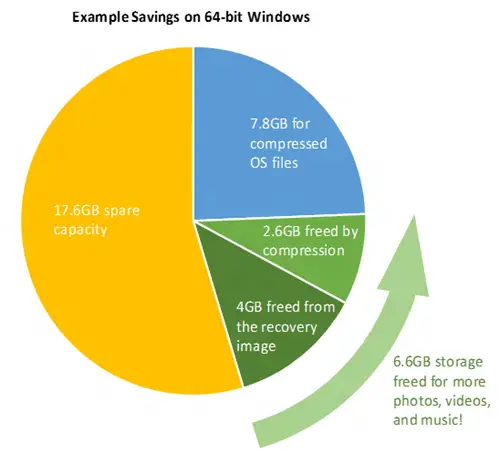
According to Microsoft, Windows employs an efficient algorithm for file compression. With the current build of Windows, the compression algorithms save up to 1.5 GB for 32-bit operating systems and at least 2.6 GB for 64-bit operating systems.
Read: Memory Compression in Windows optimizes RAM usage.
Recovery Enhancements in Windows 11/10
Normally, hardware vendors use a static recovery image so that users can revert to it when things go wrong. This static recovery image takes up a good amount of space on the hard disk drive or other storage devices. The static recovery enhancements have been eliminated completely in Windows 10 so that it occupies just a little space.
This does not mean users can no longer revert to the default state when required. The technique has changed, but not the features. The Windows Refresh and Reset features now use a technology that is dynamic. That is, Windows will reconstruct the recovery image using the inbuilt algorithms when required. This way, there is no need to store a static image of Windows. This removal of static images and building recovery images dynamically reduces the storage needs significantly in storing the operating system.
Normally, the static images take up too much space and by using dynamic recovery, Windows will save up to 12 GB of storage space on hard disk drives or other drives from where it is running. Thus, the space released by the operating system will be used by users for storing documents, photographs, videos, and music, etc.
This post shows how to compact Windows or Turn off Compact OS feature.
Smart System Compression in Windows 11/10
System compression of files in Windows need not affect the performance of the operating system in a negative way. For this purpose, compression algorithms are used that calculate how much to compress the files without posing any risk to the efficient working of Windows 11/10.
For example, Windows 11/10 takes into account the amount of RAM available and the speed of the processor on the computer being used. Based on these two factors, the system compression algorithms in Windows check out how much time it takes to decompress the files for processing them. The time taken to retrieve the file, decompress them and process them should be much smaller than what a human can perceive. The compression algorithms in Windows do just that. This means that the amount of compression would be different on different machines. A machine with a faster processor will see low usage of space by the operating system while on a slow computer system, the operating system will take up more space.
Thus, not only does Windows 11/10 use intelligent algorithms to reduce system footprint, it also saves space for Windows apps. If the system files are compressed, app files are also compressed the same way so that they can provide more on systems with lower storage capacities.
Nice article! This is great news! I cannot wait for win10. I am currently running it in a VM and have been impressed with it’s performance and usability!