XMP contains different memory profiles and allows you to switch between them. The best thing about this is that it allows you to tweak your memory’s frequency, voltage, and timing. However, we have noticed that sometimes, Windows computers won’t boot after enabling XMP. This post will discuss this issue and see how to resolve it.

Why is my computer not booting after XMP profile?
One reason could be that your motherboard does not support XMP. You can also encounter this issue if the voltage configuration is not right.
Fix Windows PC won’t turn on after enabling XMP
If your Windows computer won’t boot after enabling XMP in BIOS, follow the below solutions.
- Make sure that your motherboard supports XMP
- Reset CMOS and try again
- Manually increase the speed of your RAM
- Set the voltage manually
- Replace your RAM
Let us talk about them in detail.
1] Make sure that your motherboard supports XMP
XMP is related to your RAM and not the motherboard. However, if your motherboard does not support 3200 MTS, you won’t be able to use XMP. A 3200 MTS rating means 1600MHz because the data rate doubles the frequency or clock speed in DDR RAM.
2] Reset CMOS and try again

One of the best ways to reset the BIOS is to unplug and replug the CMOS battery. It is possible that your motherboard does not support the timing that you have set in the XMP configuration. In that case, try tweaking the timing of XMP and see if that helps. To clear CMOS, you need to follow the steps mentioned below.
- Disconnect all the peripherals connected to your computer.
- Now, detach all the power sources.
- Remove the lid of your CPU, and look for the battery on the motherboard.
- The battery might be in a horizontal or vertical holder or connected to a header with a wire. If it’s in a holder, pay attention to the + and – signs on the battery. Use a medium flat-blade screwdriver to remove the battery from its connector gently. If the battery is connected to a header with a wire, disconnect the wire.
- Wait for at least an hour, then connect back the battery, turn on your computer, and then plug all the cables back
Finally, check if the issue is resolved.
3] Manually increase the speed of the RAM
The XMP profile may be causing the processor to run at a higher clock speed than specified without any necessary adjustments. Some devices, such as the Ryzen 5 3600x, have the default maximum memory speed of 3200 MHz. If using RAM with speeds greater than 3200 MHz, the XMP profile might try to run the system faster than the specification. If the system fails to boot three times due to memory issues, the BIOS will offer the option to reset to defaults. You can reset the CMOS to get the system running and then access the BIOS. Once in the BIOS, you can select the XMP Profile and manually set the RAM speed to the default maximum of 3200 MHz. If successful, you can adjust the RAM settings to achieve the full RAM speed specification without overclocking the CPU.
4] Set the voltage manually
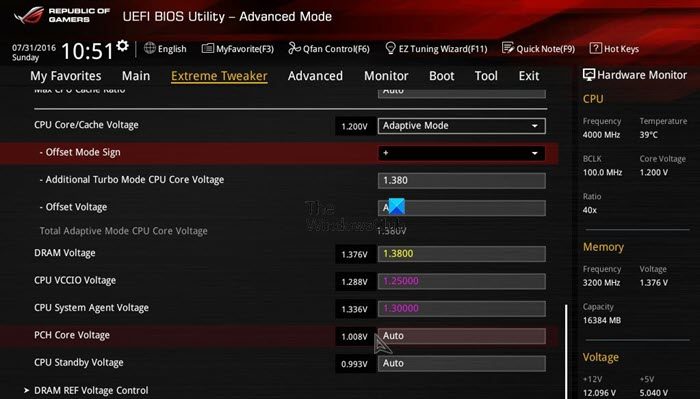
If nothing works, we will manually set the voltage and try to enable XMP. To do so, open BIOS and then make the following changes.
- Dram Voltage – 1.40v
- Dram VDDQ voltage – 1.40v
- CPU System Agent voltage – 1.28v
- IVR Transmitter VDDQ voltage – 1.40v (Advanced Memory Voltages)
- Memory Controller voltage 1.38v (Advanced Memory Voltages)
Finally, check if the issue persists.
5] Replace your RAM
If all else fails, we recommend you test your RAM. If you have two memory sticks, keep one of them plugged in and see if your system boots up. If it doesn’t start, plug it back, unplug the other one, and see if that helps. If neither of them works, borrow a RAM from your friend and plug it back, or plug your RAM into a different system to test them out. If you conclude that either both or one of your RAMs are not working, you must get a new one or send your motherboard for a repair.
Hopefully, you are able to resolve the issue using the solutions mentioned here.
Read: Fix XMP not working on Windows computer.
Can enabling XMP cause problems?
Enabling XMP (Extreme Memory Profile) can lead to risks such as system instability, overheating, and hardware damage due to increased memory speed and voltage. However, if you do a bit of research about your motherboard and RAM, you can find out if there is room for instability.