Some update files are missing, Error 0x80070003 can occur on a Windows computer when running Windows Update, activating Windows Firewall, Application Guard or Windows Sandbox, WSL, or downloading from the Microsoft Store. In this article, we will talk about Windows Update error 0x80070003. This usually means that the Windows Update (WUAUSERV) is not started or Background Intelligent Transfer Service (BITS) cannot be started. The issue could also be with other supporting components for the Windows Update mechanism.
Fix Windows Update error 0x80070003
Some effective fixes to get rid of error code 0x80070003 for Windows Updates on Windows 11/10 would be:
- Run Windows Update Troubleshooter.
- Replace old Configuration file Spupdsvc.exe
- Reset Windows Update related folders
- Check the status of Windows Update-related Windows Services
- Use System File Checker
- Reset Windows Update component to default
- Use DISM Tool to fix corrupted Windows Update files.
1] Use Windows Update Troubleshooter
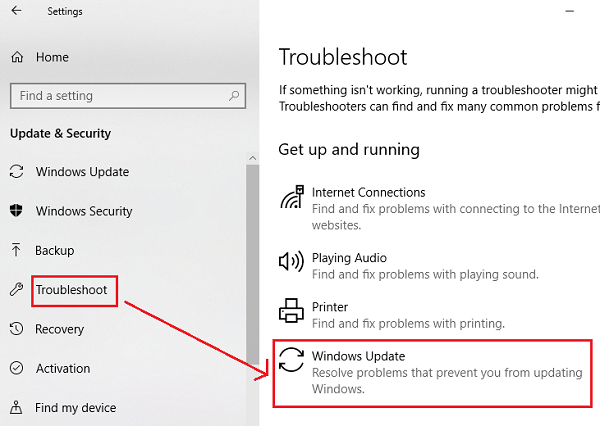
The Windows Update Troubleshooter or Microsoft’s Online Windows Update Troubleshooter can be used to detect and fix any conflicts for Windows Updates automatically.
2] Replace old Configuration file Spupdsvc.exe
Spupdsvc.exe is a process file that comes under Microsoft Update RunOnce Service. When an update becomes available for the computer, the process responsible for performing the upgrade is notified. Also, a RunOnce entry is added to the registry for spupdsvc.exe. The process is executed when the computer restarts, and the user logs on.
Open Command Prompt as an administrator to execute the following command:
cmd /c ren %systemroot%\System32\Spupdsvc.exe Spupdsvc.old
It will replace the old configuration of Spupdsvc.exe with a fresh one. Try to rerun Windows Updates and check if your issue t is fixed now.
3] Manually reset Windows Update related folders
This method is all about deleting the contents of the SoftwareDistribution folder & reset the Catroot2 folder.
The SoftwareDistribution folder and the Catroot2 folder contain some temporary system files that are responsible for applying updates to a computer. They include data that support Windows Updates as well as installers for new components.
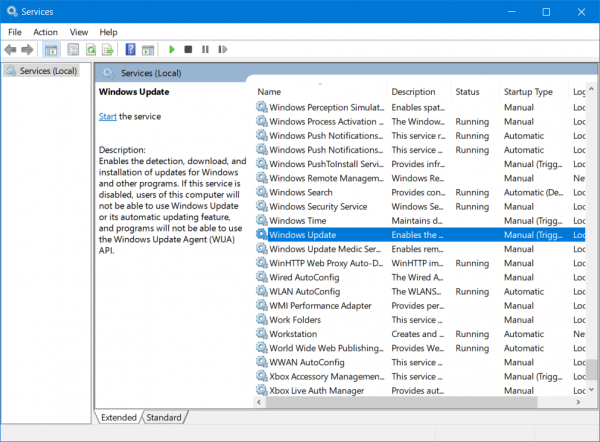
4] Check the status of Windows Update-related Windows Services
There are various Windows Services that help the functioning of different elements inside of the Windows 10 operating system. Therefore, you might need to check on the services that support Windows Updates.
Open the Windows Services Manager and locate the following services:
- Windows Update Service – Manual (Triggered)
- Background Intelligent Transfer Service – Manual.
- Cryptographic Services – Automatic
- Workstation Service – Automatic.
Open their Properties and ensure that their Startup type is as mentioned above against their name and that the Services are running. If not click on the Start button.
5] Use System File Checker
Open Command Prompt as an administrator and execute the following command:
sfc /scannow
It will run the System File Checker.
Reboot your computer after the scan has completed and run Windows Update.
6] Reset Windows Update components
Reset Windows Update component to default and see if that helps.
7] Use DISM Tool to fix corrupted Windows Update files
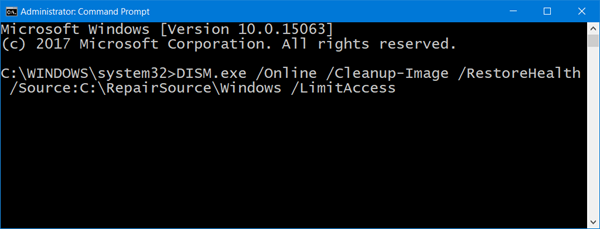
Run the DISM Tool to fix corrupted Windows Update files. If your Windows Update client is already broken, you will be required to use a running Windows installation as the repair source or use a Windows side-by-side folder from a network share, as the source of the files.
The update should be getting downloaded now!
Related: Fix Windows Backup or Restore failed error 0x80070003.
What is Error code 0x80070003 on system restore?
Error code 0x80070003 during system restore usually indicates corrupted system files on your PC. To fix this, use the System File Checker tool, which scans and repairs corrupted files, resolving the error and allowing system restore to proceed smoothly.
What is Error 0x80070003, The system Cannot find the path specified?
Error 0x80070003, “The system cannot find the path specified,” typically indicates a problem where a file or directory is missing or misnamed, especially during package loading in applications like SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS). Ensure file paths are correct and accessible to resolve the issue.
Leave a Reply