It’s always cool to work with a command prompt, batch file, etc. I still love to do a lot of work with command prompts and automate things with batch files. In this article, I will list you WMI Commands (Windows Management Instrumentation) that would be helpful to run a query within Windows 11/10/8/7 for various purposes.
Is WMIC available in Windows 11?
Microsoft has deprecated the WMIC feature and disabled it by default on Windows 11 Insider builds starting from January 29, 2024. Originally WMIC was deprecated in 2016 on Windows. Since then, it is available as a Feature on Demand (FoD) as a part of Windows 11 22H2. FoDs can be added to Windows 11 anytime and work on them. Feature on Demand is enabled by default on Windows 11 versions 22H2 and later. But, starting from January 29, 2024, they are disabled by default starting with the insider builds of Windows 11.
Windows Management Instrumentation Command-line or WMIC
Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) is the infrastructure for management data and operations on Windows-based operating systems. You can write WMI scripts or applications to automate administrative tasks on remote computers, but WMI also supplies management data to other parts of the operating system and products, for example, System Center Operations Manager.
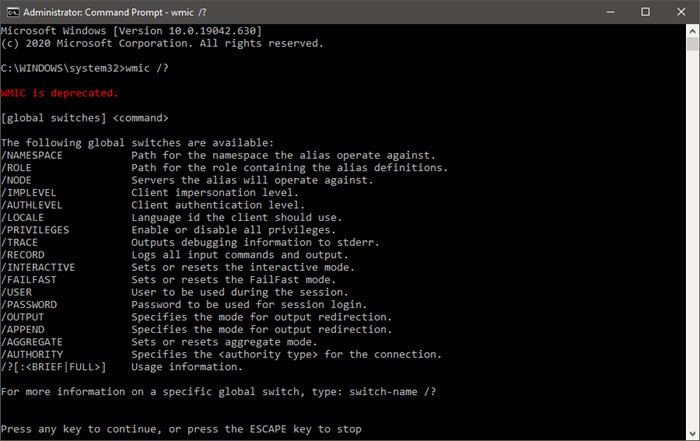
The following global switches are available:
/NAMESPACE Path for the namespace the alias operate against.
/ROLE Path for the role containing the alias definitions.
/NODE Servers the alias will operate against.
/IMPLEVEL Client impersonation level.
/AUTHLEVEL Client authentication level.
/LOCALE Language id the client should use.
/PRIVILEGES Enable or disable all privileges.
/TRACE Outputs debugging information to stderr.
/RECORD Logs all input commands and output.
/INTERACTIVE Sets or resets the interactive mode.
/FAILFAST Sets or resets the FailFast mode.
/USER User to be used during the session.
/PASSWORD Password to be used for session login.
/OUTPUT Specifies the mode for output redirection.
/APPEND Specifies the mode for output redirection.
/AGGREGATE Sets or resets aggregate mode.
/AUTHORITY Specifies the <authority type> for the connection.
/?[:<BRIEF|FULL>] Usage information.
For more information on a specific global switch, type: switch-name /?
Read: WMIC command give Access is denied error when connecting remotely
The following alias/es are available in the current role:
ALIAS - Access to the aliases available on the local system
BASEBOARD - Base board (also known as a motherboard or system board)
management.
BIOS - Basic input/output services (BIOS) management.
BOOTCONFIG - Boot configuration management.
CDROM - CD-ROM management.
COMPUTERSYSTEM - Computer system management.
CPU - CPU management.
CSPRODUCT - Computer system product information from SMBIOS.
DATAFILE - DataFile Management.
DCOMAPP - DCOM Application management.
DESKTOP - User's Desktop management.
DESKTOPMONITOR - Desktop Monitor management.
DEVICEMEMORYADDRESS - Device memory addresses management.
DISKDRIVE - Physical disk drive management.
DISKQUOTA - Disk space usage for NTFS volumes.
DMACHANNEL - Direct memory access (DMA) channel management.
ENVIRONMENT - System environment settings management.
FSDIR - Filesystem directory entry management.
GROUP - Group account management.
IDECONTROLLER - IDE Controller management.
IRQ - Interrupt request line (IRQ) management.
JOB - Provides access to the jobs scheduled using the schedule service
LOADORDER - Management of system services that define execution dependencies.
LOGICALDISK - Local storage device management.
LOGON - LOGON Sessions.
MEMCACHE - Cache memory management.
MEMORYCHIP - Memory chip information.
MEMPHYSICAL - Computer system's physical memory management.
NETCLIENT - Network Client management.
NETLOGIN - Network login information (of a particular user) management.
NETPROTOCOL - Protocols (and their network characteristics) management.
NETUSE - Active network connection management.
NIC - Network Interface Controller (NIC) management.
NICCONFIG - Network adapter management.
NTDOMAIN - NT Domain management.
NTEVENT - Entries in the NT Event Log.
NTEVENTLOG - NT eventlog file management.
ONBOARDDEVICE - Management of common adapter devices built into
the motherboard (system board).
OS - Installed Operating System/s management.
PAGEFILE - Virtual memory file swapping management.
PAGEFILESET - Page file settings management.
PARTITION - Management of partitioned areas of a physical disk.
PORT - I/O port management.
PORTCONNECTOR - Physical connection ports management.
PRINTER - Printer device management.
PRINTERCONFIG - Printer device configuration management.
PRINTJOB - Print job management.
PROCESS - Process management.
PRODUCT - Installation package task management.
QFE - Quick Fix Engineering.
QUOTASETTING - Setting information for disk quotas on a volume.
RDACCOUNT - Remote Desktop connection permission management.
RDNIC - Remote Desktop connection management on a specific
network adapter.
RDPERMISSIONS - Permissions to a specific Remote Desktop connection.
RDTOGGLE - Turning Remote Desktop listener on or off remotely.
RECOVEROS - Information that will be gathered from memory when the
operating system fails.
REGISTRY - Computer system registry management.
SCSICONTROLLER - SCSI Controller management.
SERVER - Server information management.
SERVICE - Service application management.
SHADOWCOPY - Shadow copy management.
SHADOWSTORAGE - Shadow copy storage area management.
SHARE - Shared resource management.
SOFTWAREELEMENT - Management of the elements of a software product installed
on a system.
SOFTWAREFEATURE - Management of software product subsets of SoftwareElement.
SOUNDDEV - Sound Device management.
STARTUP - Management of commands that run automatically when users
log onto the computer system.
SYSACCOUNT - System account management.
SYSDRIVER - Management of the system driver for a base service.
SYSTEMENCLOSURE - Physical system enclosure management.
SYSTEMSLOT - Management of physical connection points including ports,
slots and peripherals, and proprietary connections points.
TAPEDRIVE - Tape drive management.
TEMPERATURE - Data management of a temperature sensor (electronic thermometer).
TIMEZONE - Time zone data management.
UPS - Uninterruptible power supply (UPS) management.
USERACCOUNT - User account management.
VOLTAGE - Voltage sensor (electronic voltmeter) data management.
VOLUME - Local storage volume management.
VOLUMEQUOTASETTING - Associates the disk quota setting with a specific disk volume.
VOLUMEUSERQUOTA - Per user storage volume quota management.
WMISET - WMI service operational parameters management.
For more information on a specific alias, type: alias /?
CLASS - Escapes to full WMI schema. PATH - Escapes to full WMI object paths. CONTEXT - Displays the state of all the global switches. QUIT/EXIT - Exits the program.
Here is an example:
QFE command is something I often use to find out the list of hotfixes or security updates applied to the system.
Usage:
Open the command prompt and type in wmic qfe. This will give you the list!
Output:
Caption CSName Description HotFixID InstalledBy http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=161784 CAPTAINDBG Update KB971033 NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM http://support.microsoft.com/?kbid=2079403 CAPTAINDBG Security Update KB2079403 NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM http://support.microsoft.com/?kbid=2207566 CAPTAINDBG Security Update KB2207566 NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM http://support.microsoft.com/?kbid=2281679 CAPTAINDBG Security Update KB2281679 NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM http://support.microsoft.com/?kbid=2286198 CAPTAINDBG Security Update KB2286198 NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM http://support.microsoft.com/?kbid=2296011 CAPTAINDBG Security Update KB2296011 NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM
Also read: How to repair or rebuild the WMI Repository on Windows 11/10
What replaced WMIC?
WMIC is replaced by Windows PowerShell for WMI. Microsoft has been investing heavily in Windows PowerShell. Microsoft says they provide a more efficient way of querying WMI. It reduces the code complexity and keeps users more secure and productive.
Related read: How to use WMIC to connect to a remote computer.
Thank You :)
Shyam, This command(wmic) is there in windows XP as well. What is special in windows 7?
Cordial saludo. Interesante lo de encontrar el modelo y serial del equipo, pero por favor me podrías decir porque no me funciona? Escribo la linea de comando y la ejecuto y todo es correcto, solo que no me visualiza nada. Será porque es un equipo genérico? Gracias.
Excelente su Web Site.